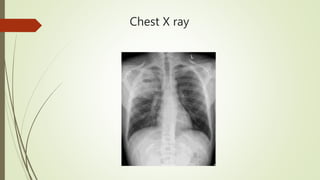
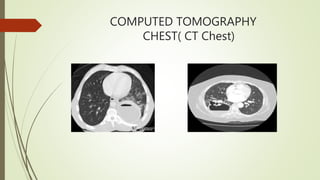
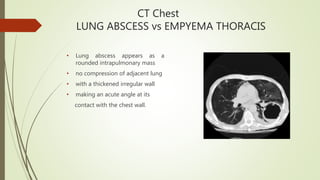
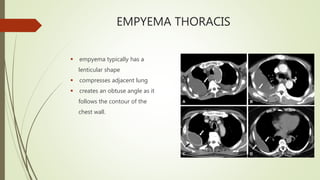
The patient is diagnosed with lung abscess based on his symptoms of productive cough, fever and chest heaviness along with abnormal chest x-ray findings. As the patient has a history of water pipe use, the lung abscess is classified as secondary and due to his COPD, it is chronic in nature. Diagnostic workup would include sputum culture, CT chest and percutaneous needle aspiration for confirmation. Treatment involves long-term IV antibiotics targeting anaerobes along with drainage and supportive care.