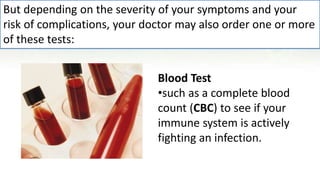
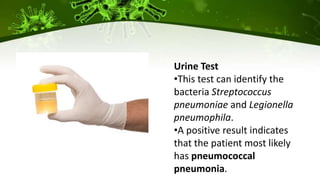
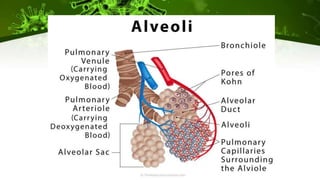
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It occurs when the alveoli in the lungs become filled with fluid or pus, making breathing painful and limiting oxygen intake. There are different classifications and types of pneumonia depending on the causative agent and where it was acquired. Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests like chest x-rays, and lab tests of sputum, blood, or fluid samples. Complications can include respiratory failure or sepsis. Treatment involves antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, antivirals for viral pneumonia, and managing symptoms at home with rest, fluids, and fever control.