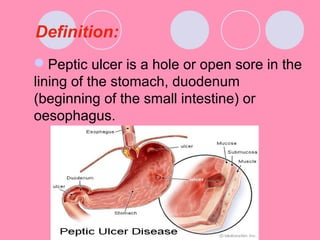
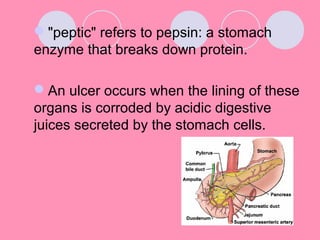
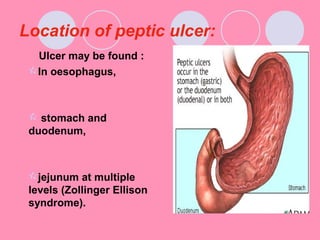
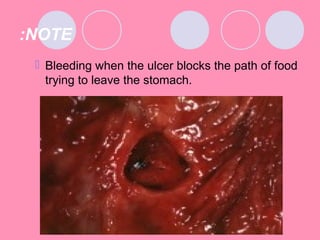
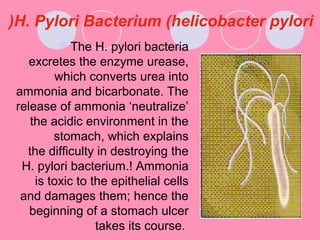
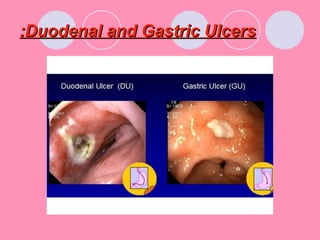
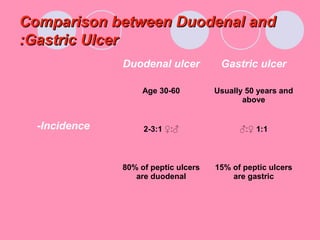
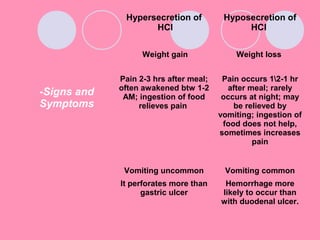
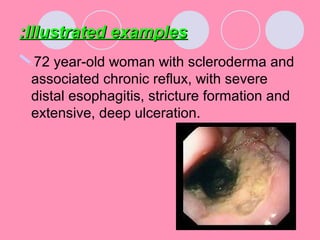
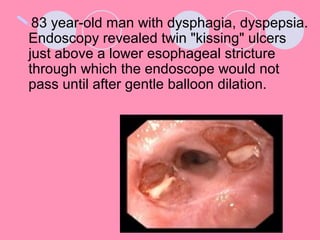
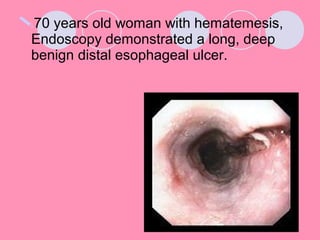
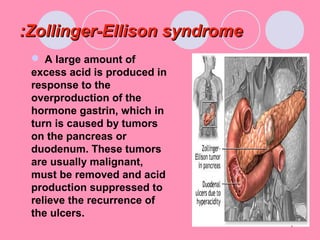
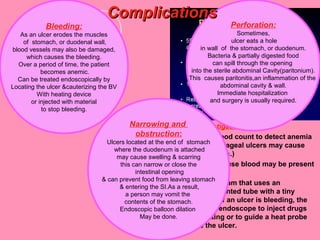
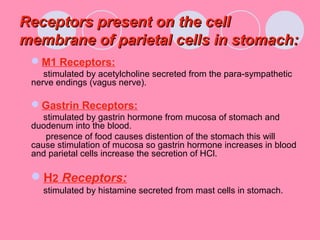
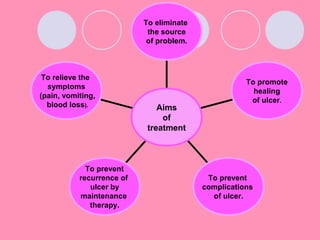
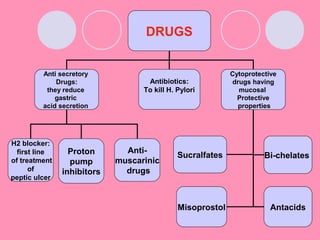
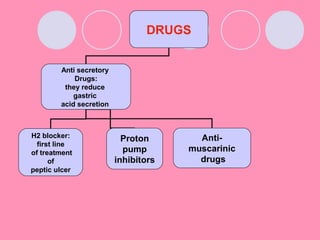
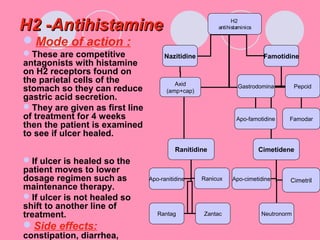
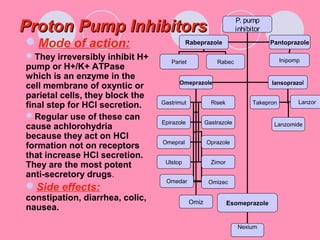
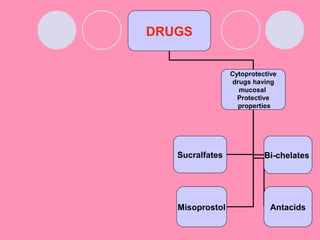
Peptic ulcers form when the lining of the stomach or duodenum is corroded by acidic digestive juices. Common symptoms include abdominal pain relieved by food or antacids. While acid contributes to ulcer formation, infection with H. pylori bacteria is now believed to be the leading cause. Other risk factors include NSAID use, smoking, alcohol, and stress. Complications can include bleeding, perforation, and narrowing or obstruction of the stomach outlet. Endoscopy allows visualization and biopsy of ulcers, while treatment aims to eliminate H. pylori infection and reduce acid secretion.