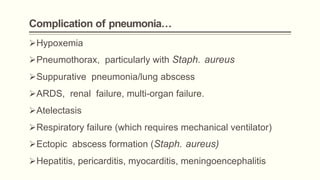
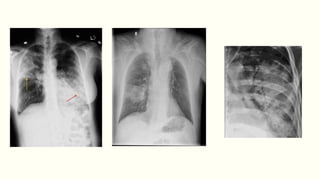
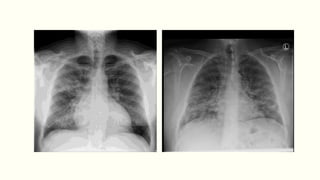
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition characterized by inflammation in the lungs and often results in significant mortality, remaining a leading cause of death globally. It can be classified into different types, such as community-acquired pneumonia and hospital-acquired pneumonia, with varied causative pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Diagnosis typically involves clinical assessment and imaging, while management focuses on oxygenation, fluid balance, and prompt antibiotic therapy depending on the severity and causative agents.






























![Management…
Uncomplicated CAP:
Outpatient Treatment (empirical)
Previously healthy and no antibiotics in past 3 months
* A macrolide (clarithromycin or azithromycin or Doxycycline )
Comorbidities or antibiotics inpast 3 months:
Respiratory fluoroquinolone [moxifloxacin ,levofloxacin ]or
β- lactam ( high-dose amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumonia-190922132637/85/Pneumonia-47-320.jpg)
![Management…
Inpatient Treatment- Non ICU:
•A respiratory fluoroquinolone [moxifloxacin ,levofloxacin ]
•β -lactam [cefotaxime ,ceftriaxone ,ampicillin] plus a
macrolide [oral clarithromycin or azithromycin)
Inpatient Treatment- ICU:
•β -lactam plus Azithromycin or a fluoroquinolone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumonia-190922132637/85/Pneumonia-48-320.jpg)
![Management…
Pseudomonas:
MRSA
• If MRSA, add linezolid or vancomycin
• An antipneumococcal, antipseudomonal β-lactam
[piperacillin/tazobactam, cefepime , imipenem ,
meropenemplus flouroquinolones]
• Above β-lactams plus an aminoglycoside and azithromycin
• Above β-lactams plus an aminoglycoside plus
an antipneumococcal fluoroquinolone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumonia-190922132637/85/Pneumonia-49-320.jpg)