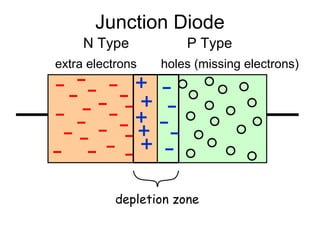
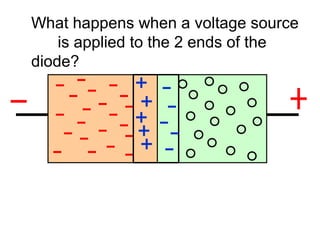
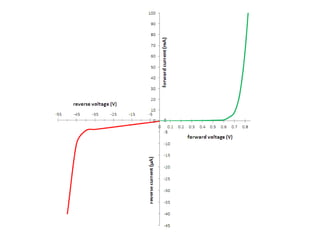
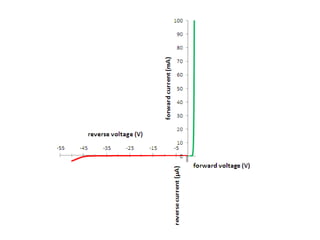
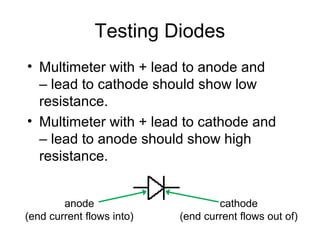
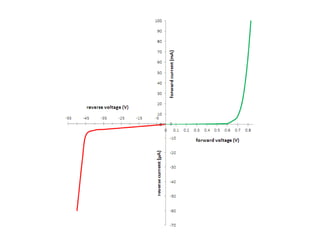
When a voltage is applied to a diode, electrons flow from the N-type side through the depletion zone and into the P-type side if the diode is forward biased. This causes current to flow. If the voltage is reversed, the depletion zone widens and no current flows, making the diode act as an open switch. Diodes can be used as rectifiers to convert AC to DC or as switches that allow current in one direction but not the other depending on bias polarity.