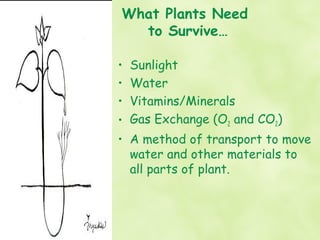
1) Plants are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that have cell walls containing cellulose. They develop from multicellular embryos and are autotrophic, producing their own food through photosynthesis.
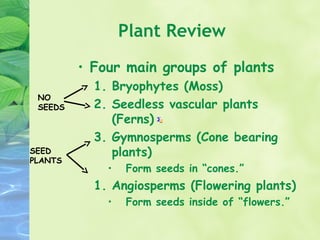
2) There are four major groups of plants: bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Angiosperms are the most common and produce seeds inside flowers.
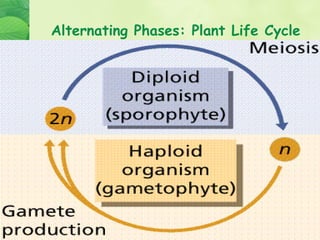
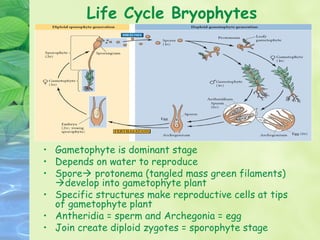
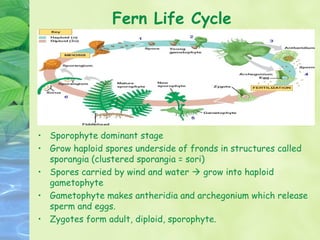
3) Plants go through life cycles that alternate between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte phases. During the gametophyte phase, gametes are produced which fuse during fertilization to form the sporophyte.