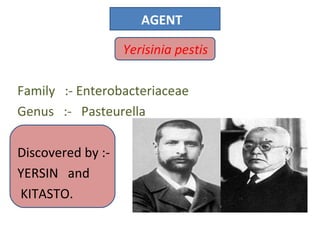
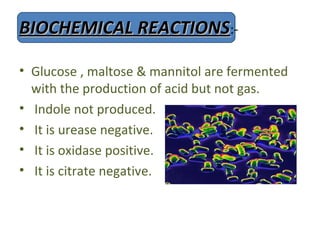
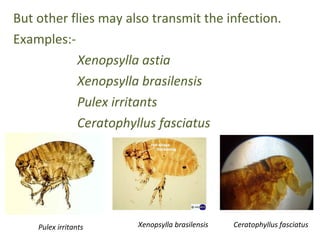
Yersinia pestis is the bacterium that causes plague. It is usually transmitted to humans by the bites of infected fleas that live on rodents. The rat flea Xenopsylla cheopsis is the most common and efficient vector. Certain environmental conditions like warm temperatures between 20-25 degrees Celsius and 60% humidity provide favorable conditions for plague transmission. Human activities and movement can also influence plague spread. Monitoring flea indices on rodents is important for evaluating plague risk and the effectiveness of control programs.