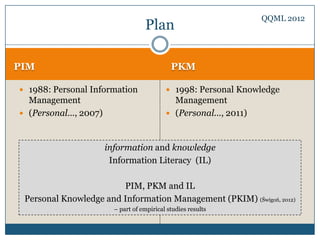
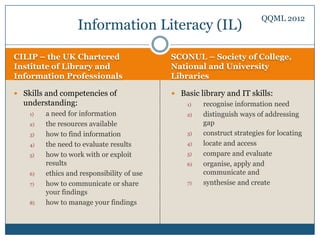
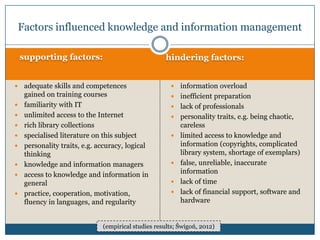
The document discusses personal knowledge and information management (PKIM) as an interdisciplinary concept critical for individuals, particularly students, in managing knowledge and information effectively. It highlights the differences between knowledge management (KM) and information management (IM), emphasizing their interconnectedness and how they contribute to successful academic and everyday life. The empirical study findings suggest that factors influencing knowledge and information management include skills, access to resources, and personality traits.