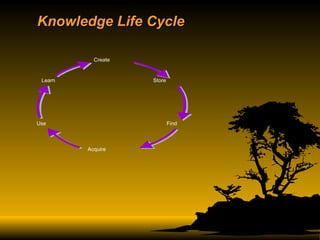
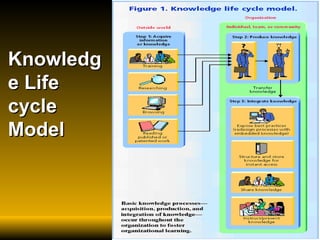
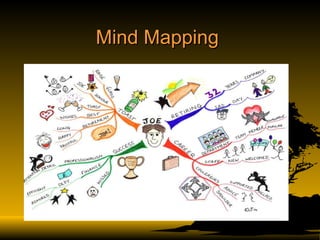
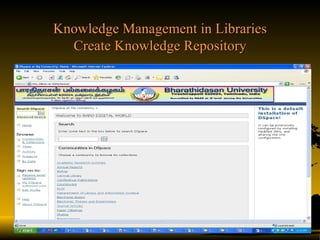
The document discusses key concepts in knowledge management including definitions, types of knowledge, knowledge life cycles, learning styles, technologies, and roles in organizations like libraries. It defines knowledge management as planning, designing, building, operating and maintaining knowledge management systems to manage both explicit and tacit knowledge. Success requires leadership, culture, infrastructure and connecting people with information and each other.
![Knowledge Management: Overview By M. SURULINATHI Assistant Librarian [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surulinathi-1233461933288328-2/75/Knowledge-Management-Overview-1-2048.jpg)