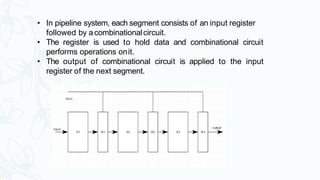
This document discusses pipelining in computer processors. It defines pipelining as accumulating instructions through a pipeline to allow storing and executing instructions in parallel. There are two main types of pipelines: arithmetic pipelines which handle floating point operations, and instruction pipelines which overlap the fetch, decode, and execute phases of instructions. Pipelining provides benefits like reduced cycle time and increased throughput, but also has disadvantages like increased complexity, costs, and instruction latency. Common issues that can interfere with pipelining are timing variations, data hazards, branching, interrupts, and data dependency.