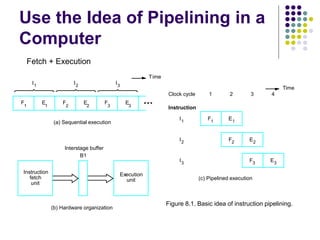
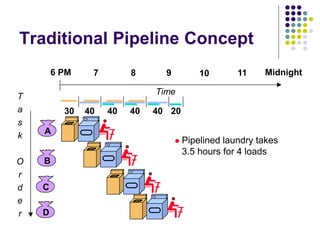
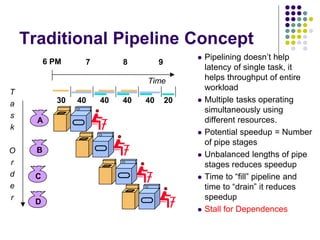
This document discusses instruction pipelining as a technique to improve computer performance. It explains that pipelining allows multiple instructions to be processed simultaneously by splitting instruction execution into stages like fetch, decode, execute, and write. While pipelining does not reduce the time to complete individual instructions, it improves throughput by allowing new instructions to begin processing before previous instructions have finished. The document outlines some challenges to achieving peak performance from pipelining, such as pipeline stalls from hazards like data dependencies between instructions. It provides examples of how data hazards can occur if the results of one instruction are needed by a subsequent instruction before they are available.




![Concept of Pipelining in
Computers
Each instruction is split into a sequence of
dependent stages:
[Fetch,Decode,Execute,Write].
The first step is always to fetch the instruction
from memory; the final step is usually writing the
results of the instruction to processor registers or
to memory.
Pipelining seeks to let the processor work on as
many instructions as there are dependent steps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pipelining-151229092158/85/Concept-of-Pipelining-10-320.jpg)