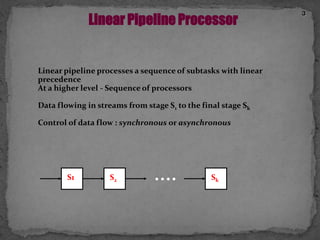
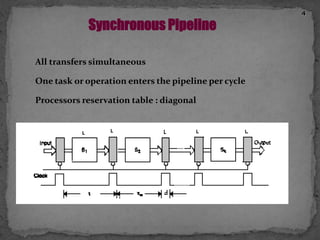
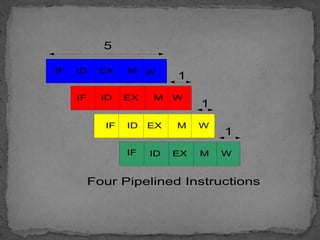
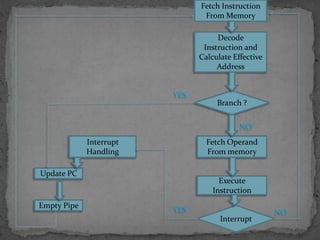
This document discusses pipelining in microprocessors. It describes how pipelining works by dividing instruction processing into stages - fetch, decode, execute, memory, and write back. This allows subsequent instructions to begin processing before previous instructions have finished, improving processor efficiency. The document provides estimated timing for each stage and notes advantages like quicker execution for large programs, while disadvantages include added hardware and potential pipeline hazards disrupting smooth execution. It then gives examples of how four instructions would progress through each stage in a pipelined versus linear fashion.