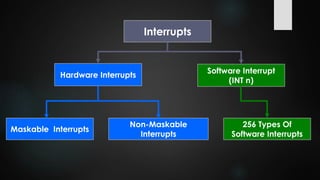
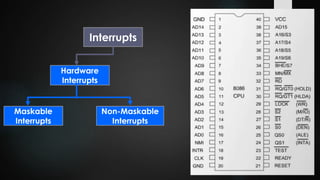
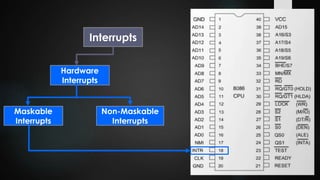
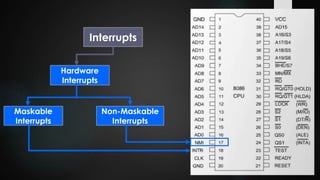
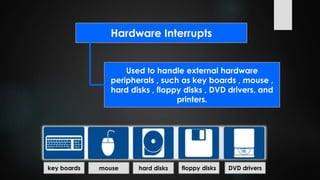
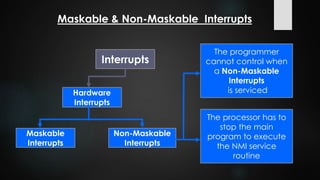
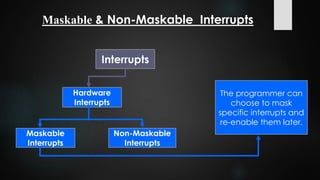
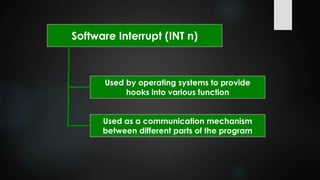
This document provides an overview of interrupts in the 8086 microprocessor. It defines an interrupt as an event that breaks normal program execution to service an interrupt request. Interrupts can be triggered by hardware signals from peripherals or software interrupt instructions. The 8086 supports hardware interrupts on the INTR and NMI pins, which can be maskable or non-maskable. It also supports 256 software interrupt types. Common uses of interrupts include servicing devices like keyboards and handling exceptions.