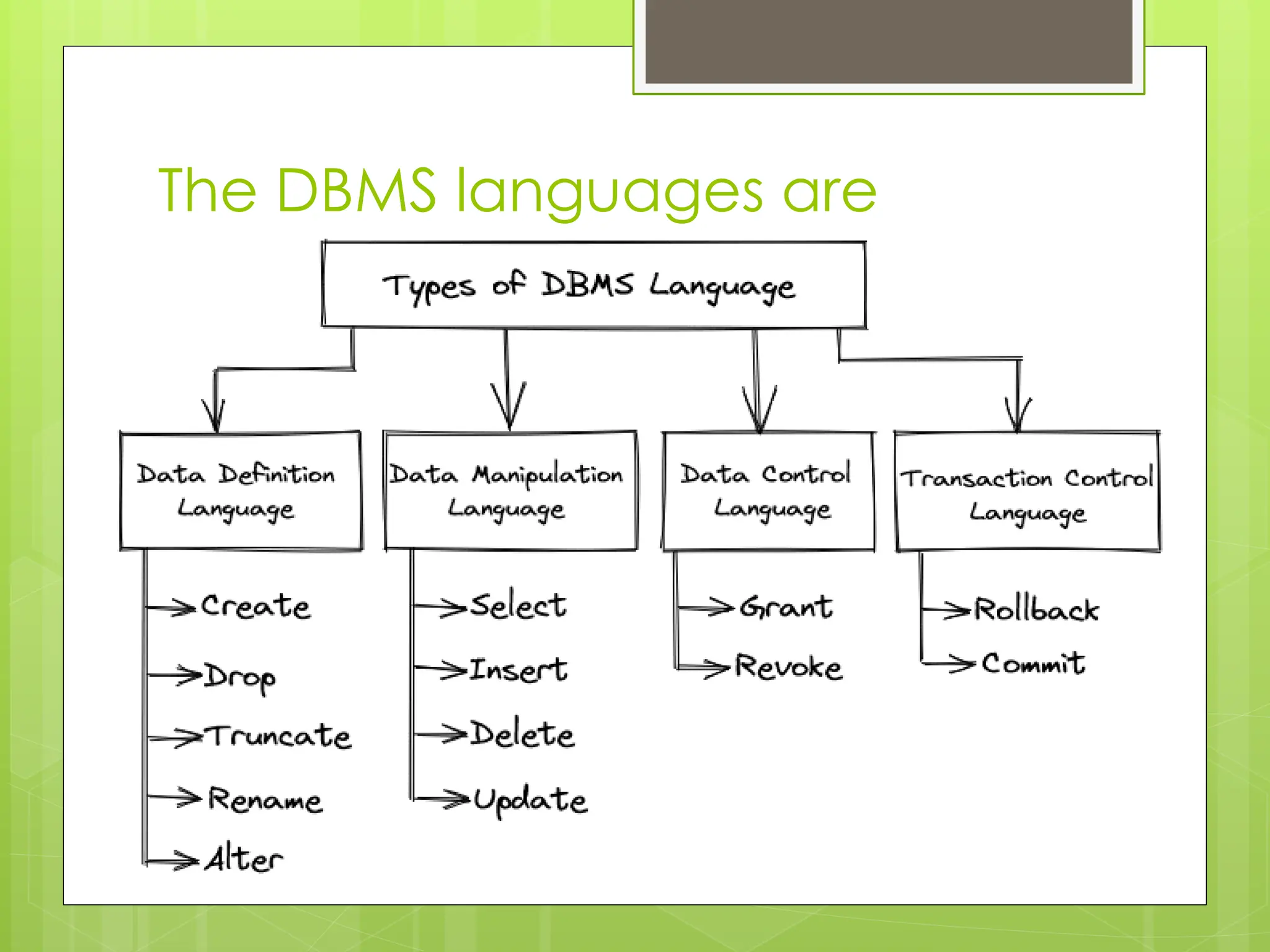
The document outlines various database languages used for managing data within a database, focusing on Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). It details commands such as CREATE, DROP, ALTER, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, along with their syntax and examples. Additionally, it explains the concepts of granting and revoking permissions, as well as committing and rolling back transactions.









![UPDATE Command
UPDATE: This command is used to update or modify the
value of a column in the table.
Syntax:
1. UPDATE table_name SET [column_name1= value1,...column
_nameN = valueN] [WHERE CONDITION]
For example:
1. UPDATE students SET User_Name = 'Sandy'
WHERE Student_Id = '3'
DELETE: It is used to remove one or more row from a table.
Syntax:
1. DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE condition];
For example:
DELETE FROM java WHERE Author=“sandy";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaselanguages-250206102314-72199cd6/75/Database-Languages-power-point-presentation-11-2048.jpg)


