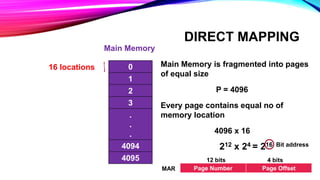
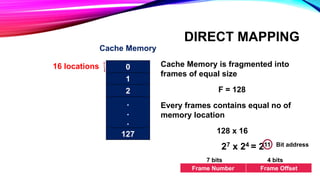
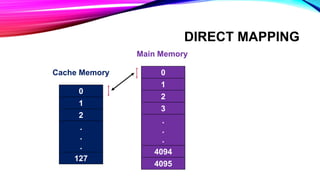
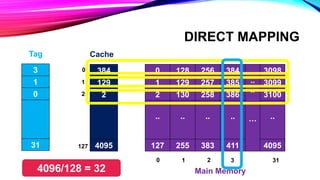
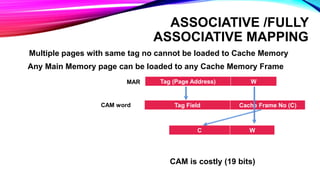
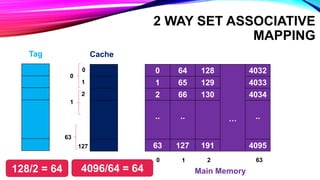
This document discusses different cache mapping techniques including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set-associative mapping. It provides examples of direct mapping where the main memory is divided into pages that map to cache frames. Direct mapping allows only one main memory page to map to each cache frame based on the page number. Associative mapping allows any main memory page to map to any cache frame by using a content addressable memory. Set-associative mapping groups cache frames into sets, and each main memory page can map to one of the frames within a set. The document also gives an example of how cache hit rates can be different between direct mapping, 2-way set associative mapping, and fully associative mapping.




![DIRECT MAPPED CACHE
sequence of block addresses: 0, 8, 0, 6, and 8.
MISS Memory [0]
MISS Memory [8]
MISS Memory [0]
MISS Memory [0] Memory [6]
MISS Memory [8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-221102145444-83927a24/85/2-Cache-Mapping-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![2 way Set Associative Mapped Cache
sequence of block addresses: 0, 8, 0, 6, and 8.
MISS Memory [0]
MISS Memory [0] Memory [8]
HIT Memory [0] Memory [8]
MISS Memory [0] Memory [6]
MISS Memory [8] Memory [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-221102145444-83927a24/85/2-Cache-Mapping-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![Fully Associative Mapped Cache
sequence of block addresses: 0, 8, 0, 6, and 8.
MISS Memory [0]
MISS Memory [0] Memory [8]
HIT Memory [0] Memory [8]
MISS Memory [0] Memory [8] Memory [6]
HIT Memory [0] Memory [8] Memory [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-221102145444-83927a24/85/2-Cache-Mapping-pptx-13-320.jpg)

