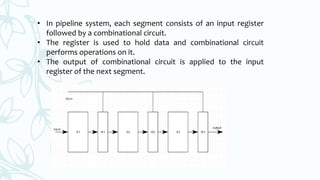
Pipelining is a technique where multiple instructions are overlapped during execution by dividing the instruction cycle into stages connected in a pipeline structure. There are two main types of pipelines - instruction pipelines which overlap the fetch, decode, and execute phases of instructions to improve throughput, and arithmetic pipelines used for floating point and fixed point operations. Pipeline conflicts can occur due to timing variations, data hazards, branching, interrupts, or data dependency which reduce the pipeline's performance. The main advantages of pipelining are reduced cycle time, increased throughput, and improved reliability, while the main disadvantage is increased complexity, cost, and instruction latency.