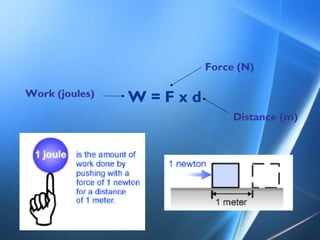
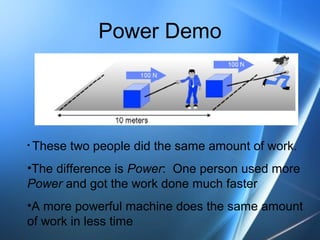
Work involves applying a force over a distance. In physics, work is defined by the formula W=Fd, where W is work, F is force, and d is distance. Examples of work include moving an object with a force of one newton over a distance of one meter, which equals one joule of work. A joule is the standard unit used to measure work. Machines like simple machines can help us do work by multiplying the force applied.