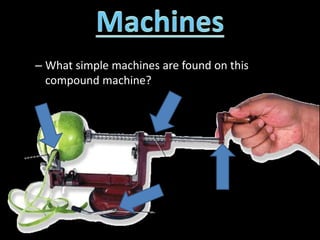
This document contains information about work, power, and machines. It includes:
1. Questions from student periods about work, power, machines, and their relationships.
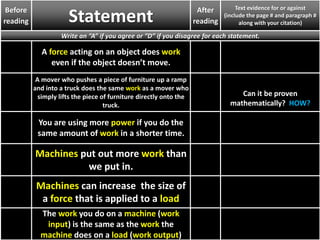
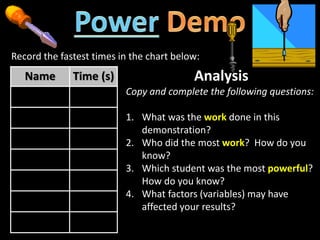
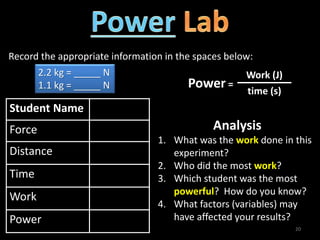
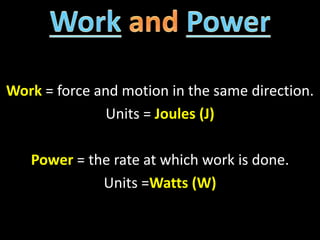
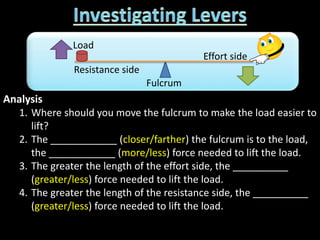
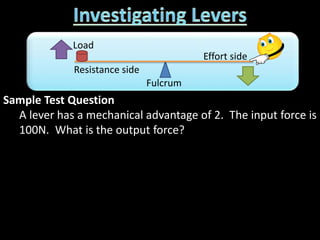
2. Definitions and formulas for work, power, and mechanical advantage. Work is force times distance, power is the rate of work, and mechanical advantage is the output force divided by the input force.
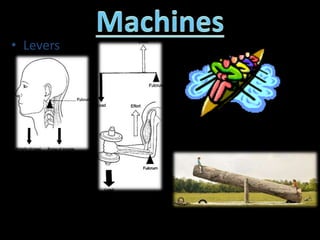
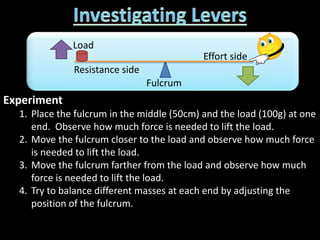
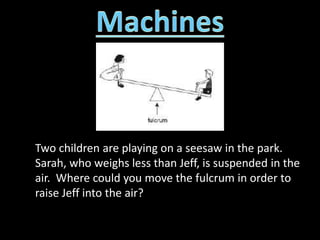
3. Examples of calculating work, power, mechanical advantage, and mechanical efficiency for simple machines like levers, pulleys, and wedges.