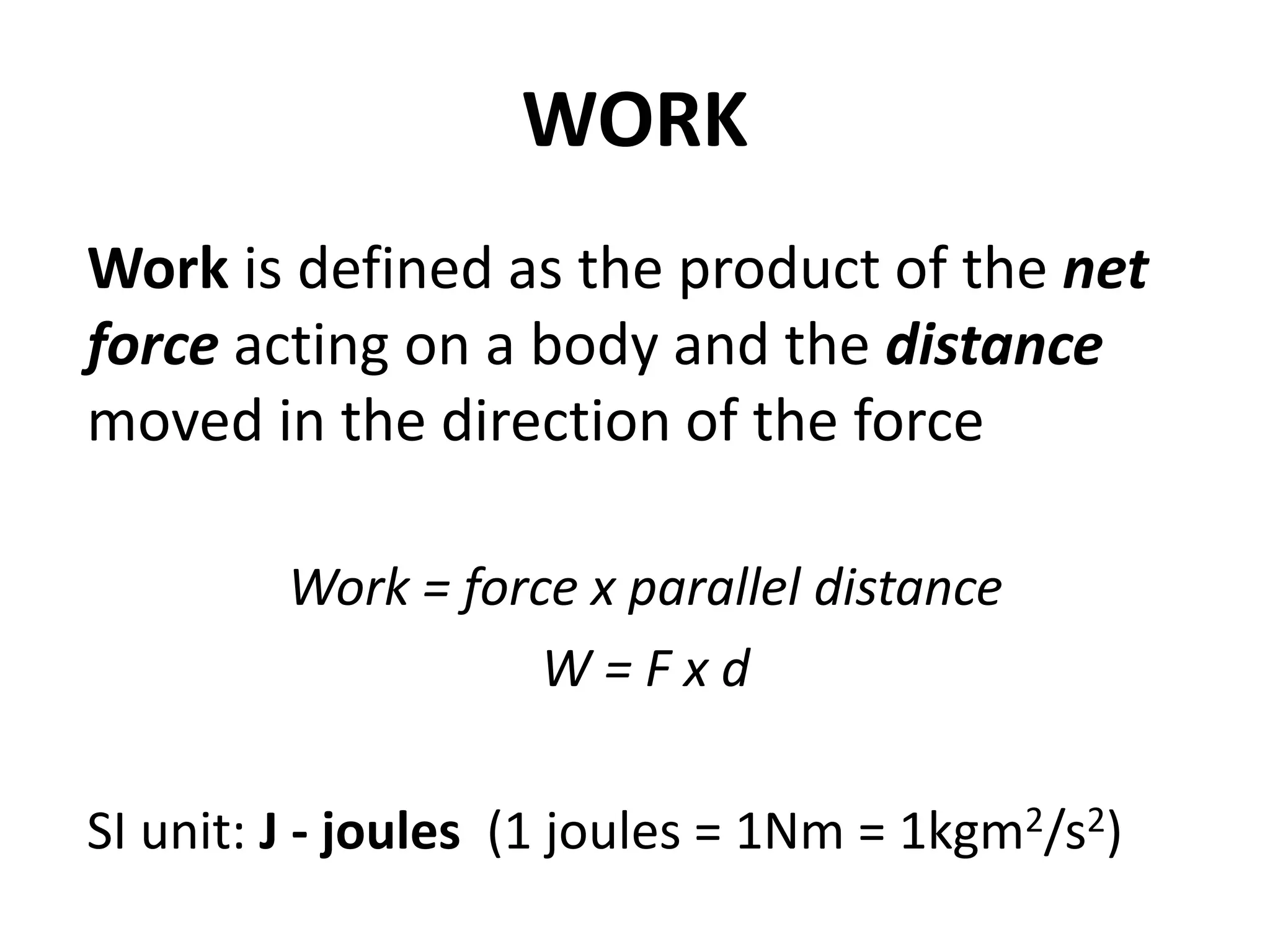
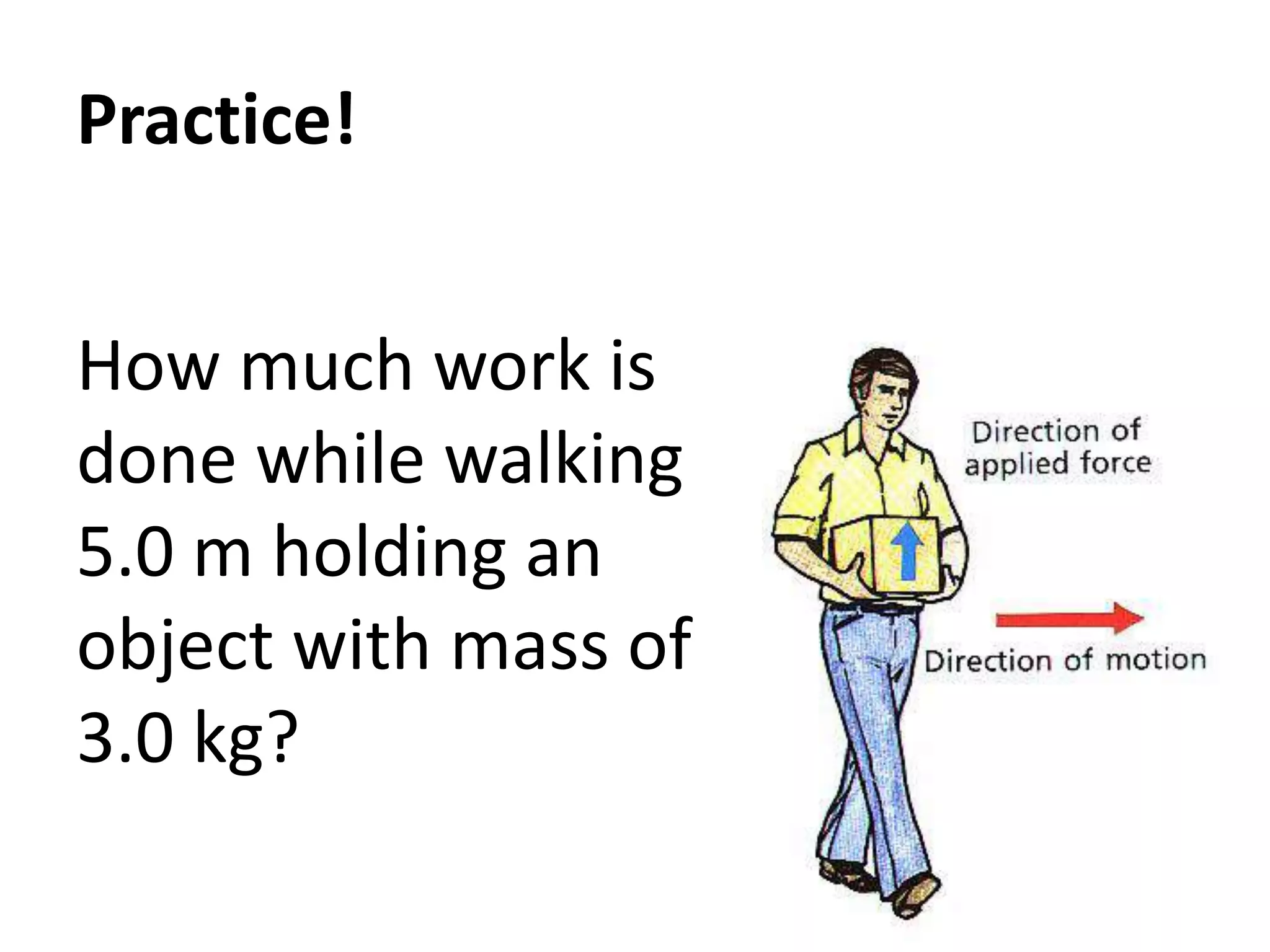
1) Work is defined as the product of the net force acting on a body and the distance moved in the direction of the force. The SI unit for work is the joule.
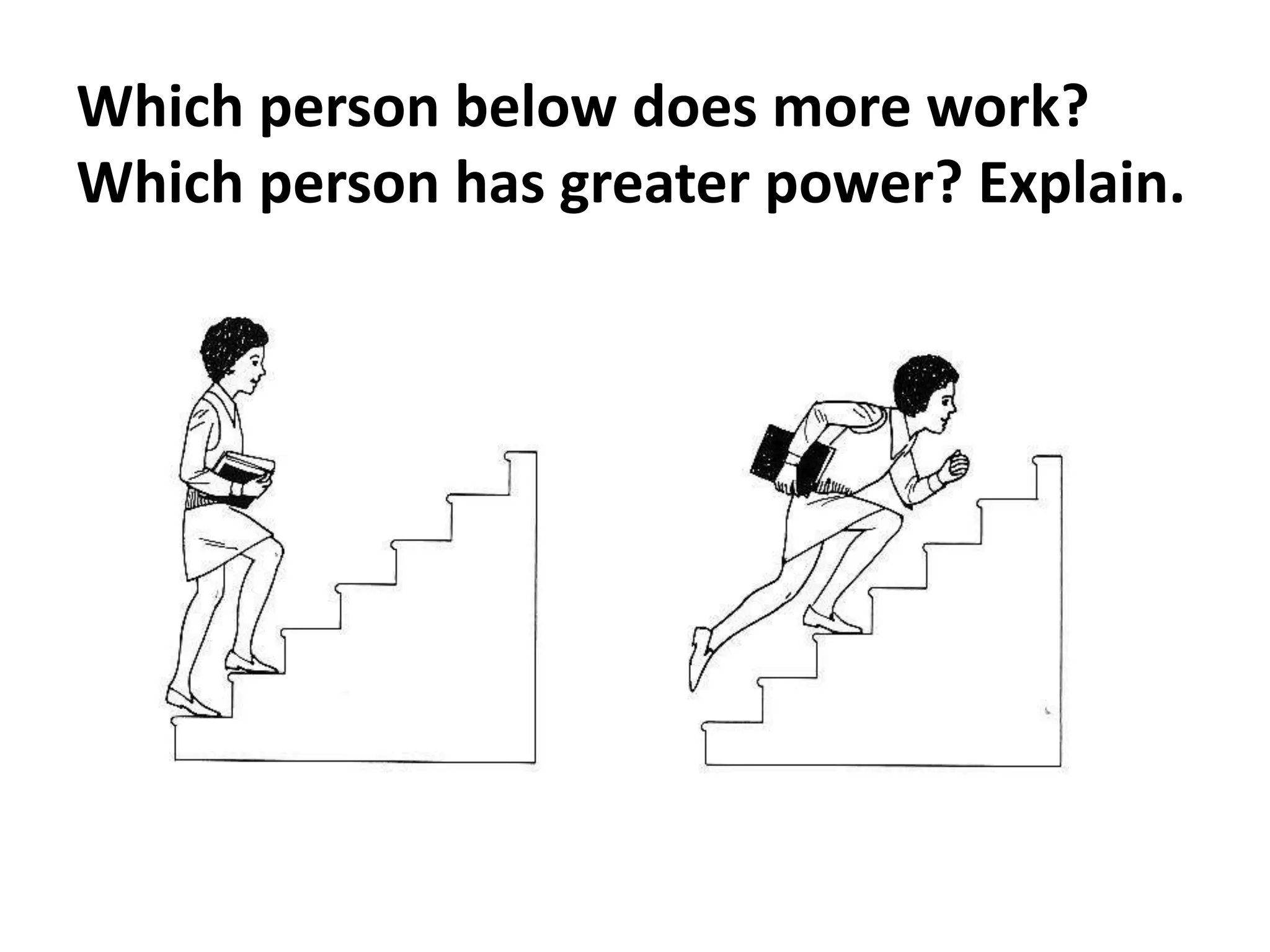
2) Power is defined as the rate at which work is done. It is measured in watts, which are equal to one joule per second.
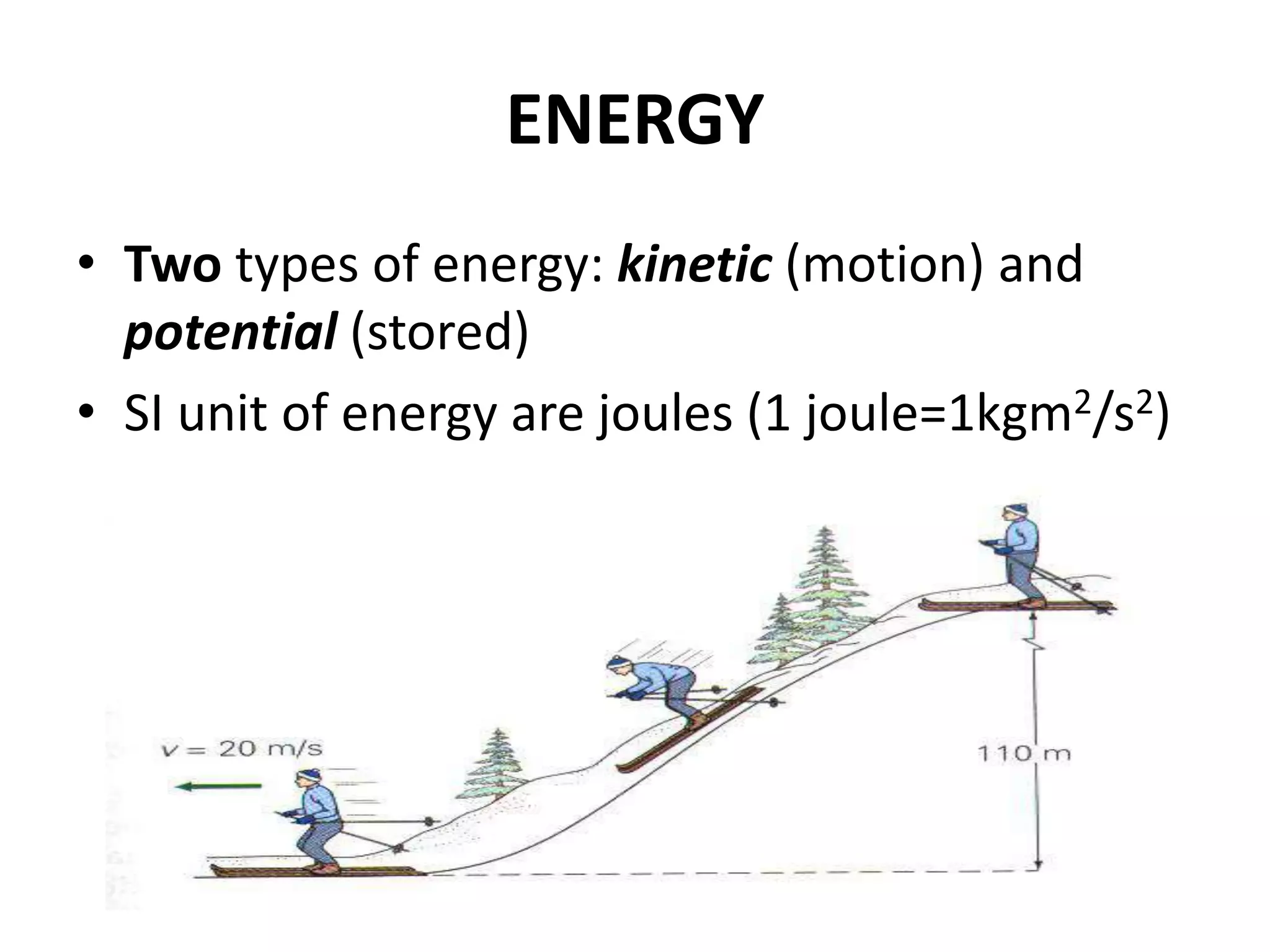
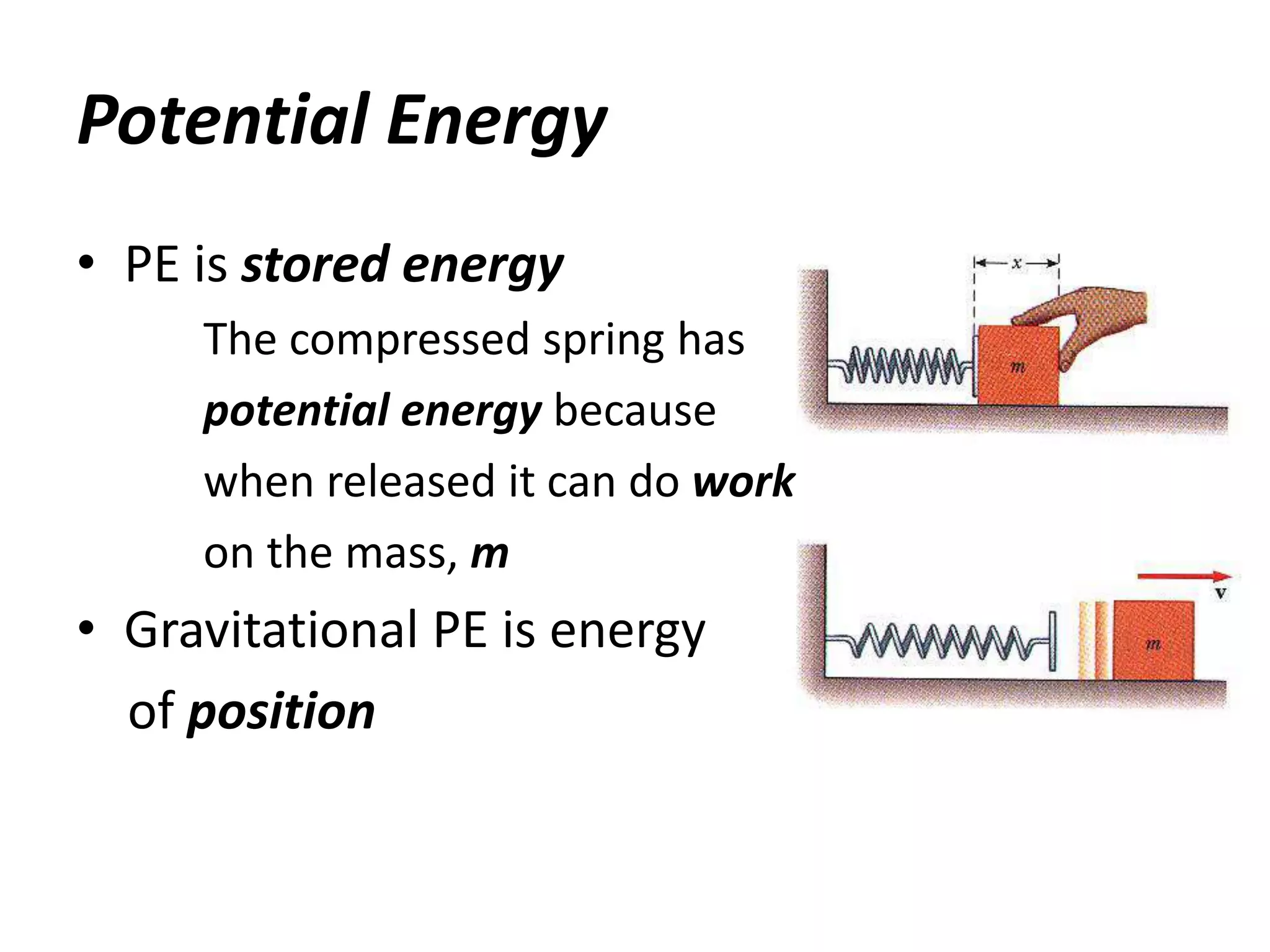
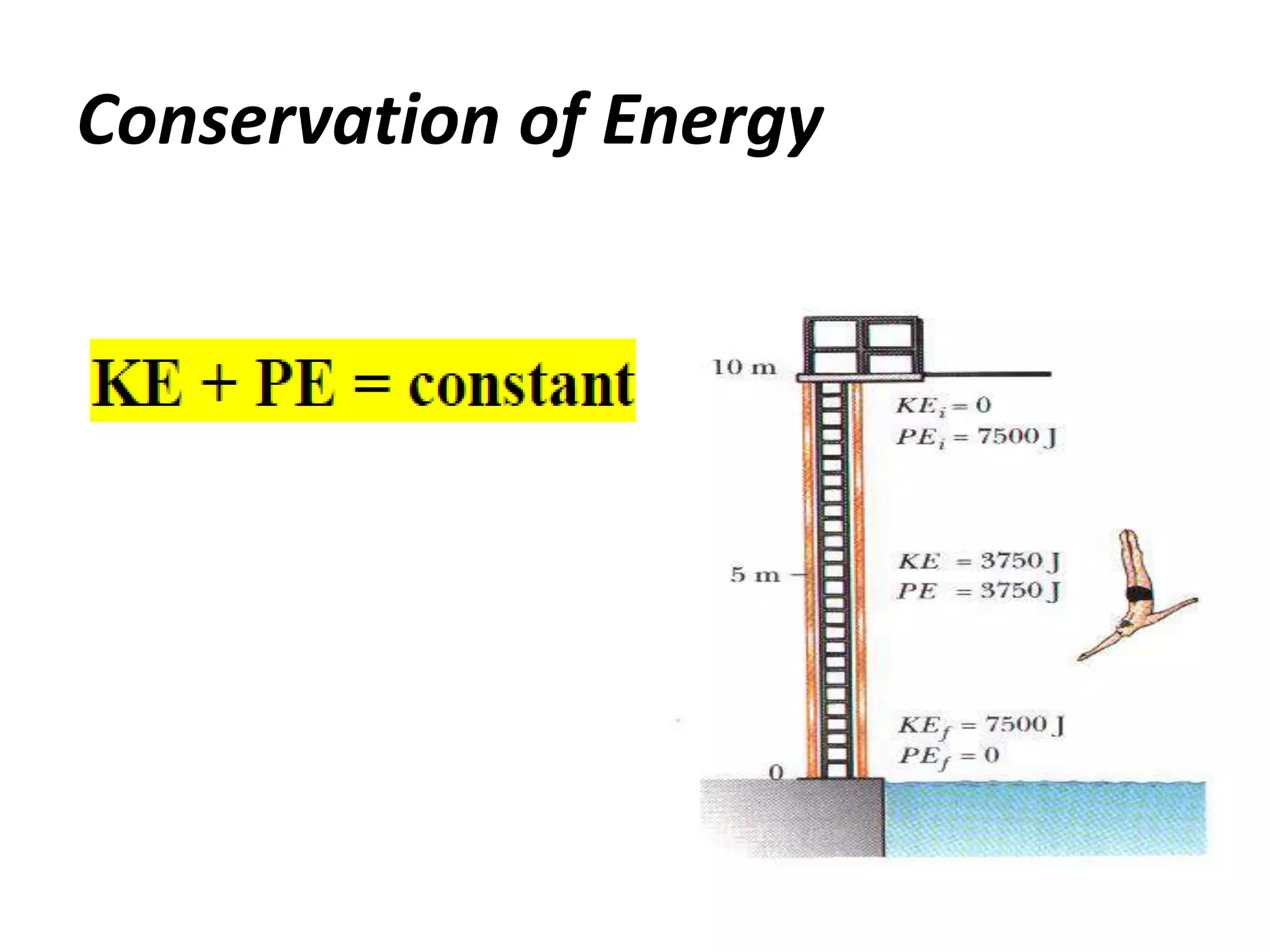
3) There are two main types of energy: kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy due to an object's position or composition. The SI unit for both is the joule. According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy in an isolated system remains constant.