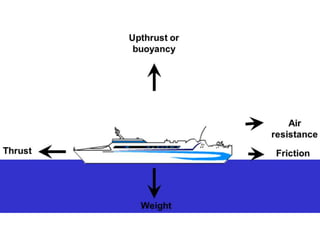
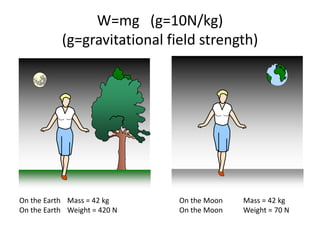
Forces can start, stop, or change the motion of objects. There are two main types of forces - contact forces, which require touching objects, like pushing or pulling, and non-contact forces, which act over a distance without touching, like magnetic or gravitational forces. Forces are measured in units called newtons. Forces can be balanced, where opposing forces cancel each other out, or unbalanced, where a net force causes motion or changes the motion of an object. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force of gravity acting on an object's mass.