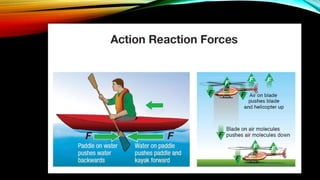
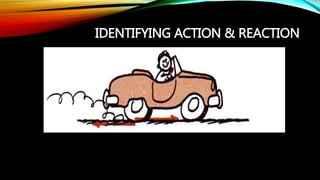
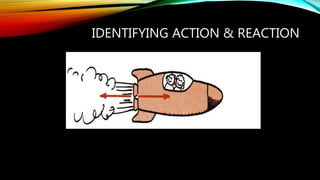
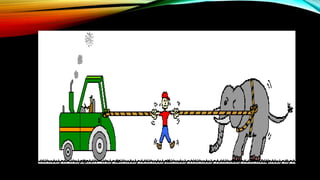
1) Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
2) Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force back on the first object. These paired forces are called action-reaction force pairs.
3) Examples of action-reaction force pairs include a rocket exhaust pushing down on gases which push back up on the rocket with an equal force, and a car tire pushing down on the road surface while the road pushes back up on the tire.