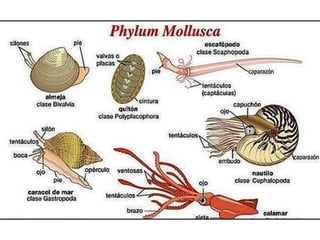
This document provides information about the phylum Mollusca. It discusses the 7 main classes of molluscs:
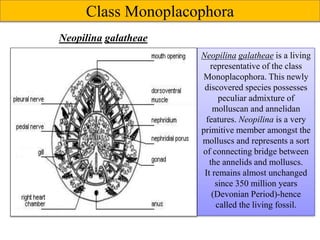
1) Monoplacophora - Contains only the genus Neopilina and is considered a "living fossil".
2) Aplacophora - Wormlike molluscs without a shell.
3) Polyplacophora - Contains chitons which have 8 overlapping shell plates.
4) Scaphopoda - Marine molluscs known as tusk shells that burrow into sediments.
5) Gastropoda - The largest class containing snails and slugs.
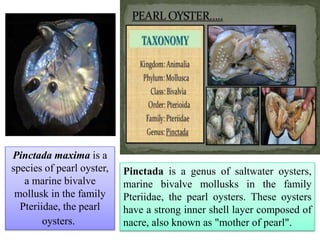
6) Bivalvia - Contains clams, oyst