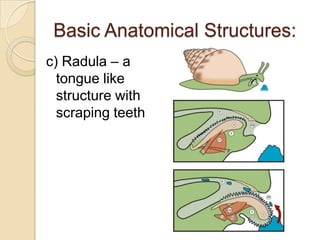
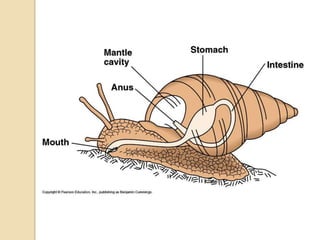
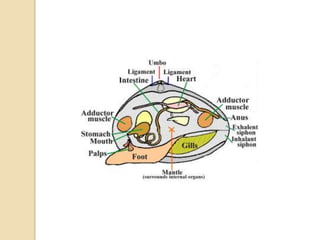
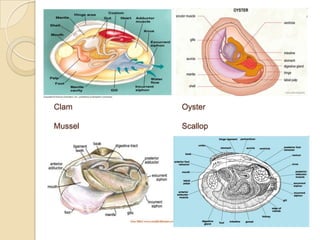
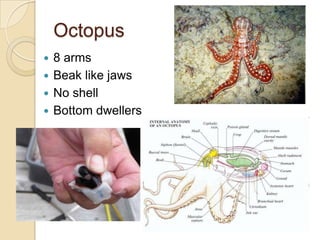
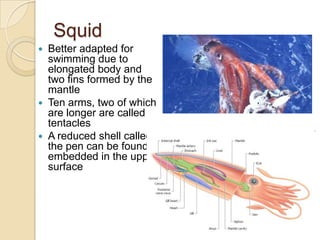
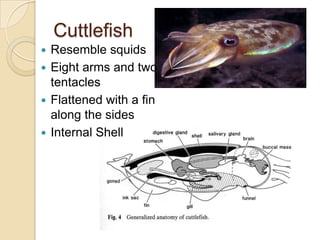
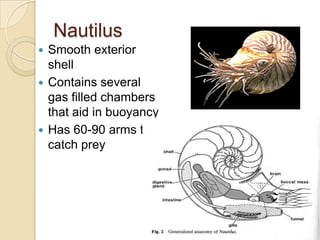
Mollusks are a diverse phylum with over 50,000 species across 10 classes. They include squid, octopus, clams, snails, and oysters. Mollusks have a mantle, foot, and radula as basic anatomical structures. The foot is adapted for movement and the mantle circulates water and secretes shells. Gastropoda includes snails and slugs with a radula and sometimes a shell. Bivalvia includes clams and oysters with two hinged shells and siphons. Cephalopoda are advanced mollusks like squid and octopus with specialized features for swimming including fins or jet propulsion.