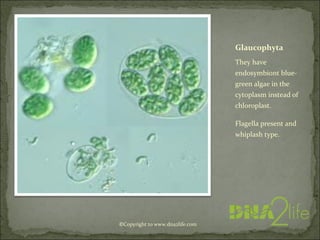
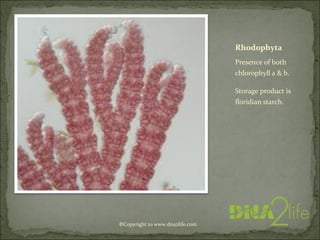
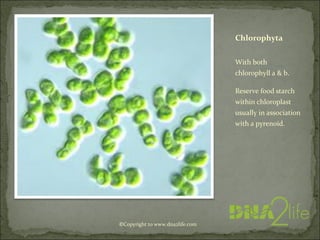
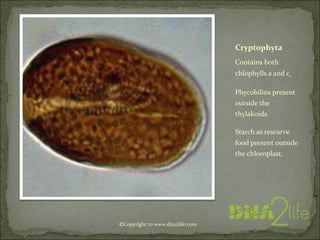
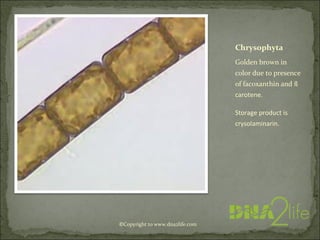
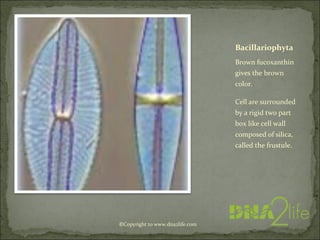
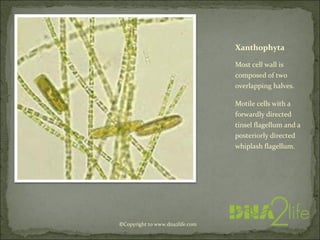
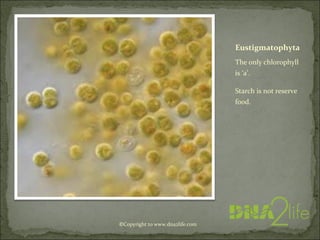
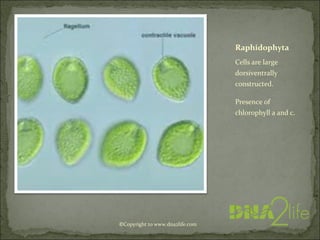
Phycology is the study of algae. Algae range from microscopic to large seaweeds, are mostly photosynthetic, and belong to the kingdom Protista. They are classified based on characteristics like cell structure, cell wall composition, food reserves, and flagella. There are many systems for classifying algae into phyla, including Cyanophyta, Rhodophyta, Chlorophyta, and others, which differ in their pigments, food storage, and cellular structure.