Embed presentation
Download to read offline



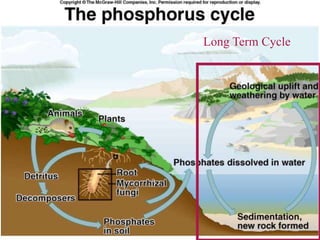

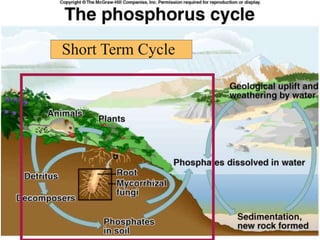


The phosphorus cycle describes how phosphorus moves through the biosphere and lithosphere. Phosphorus is essential for life and is found in cell membranes, ATP, and bones. It cycles through geological and biological processes, with the long term cycle involving the weathering of phosphorus-containing rocks and the short term cycle moving phosphorus through ecosystems via photosynthesis, decomposition, and the food chain.






