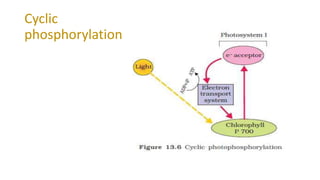
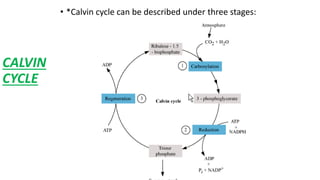
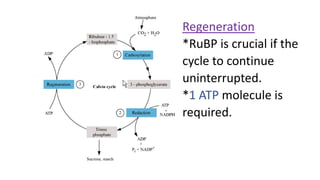
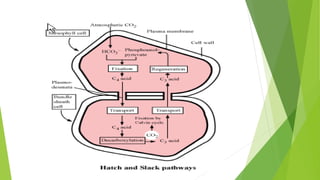
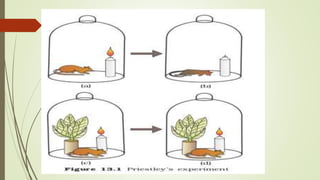
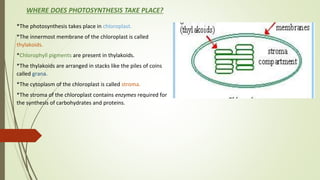
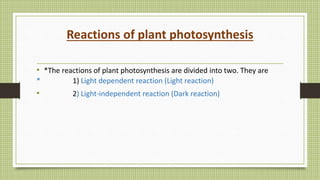
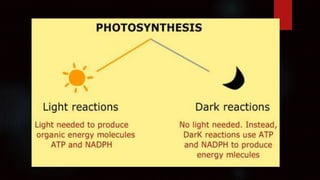
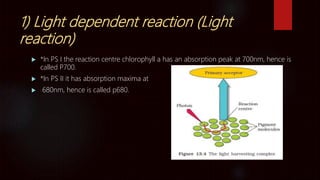
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It takes place in two stages - the light dependent reaction which uses energy from sunlight to convert water to oxygen and produces ATP and NADPH, and the light independent reaction (Calvin cycle) which uses ATP and NADPH to incorporate carbon from carbon dioxide into organic compounds. There are several factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis including light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and water availability.






![ELECTRON
TRANSPORT
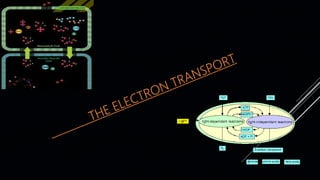
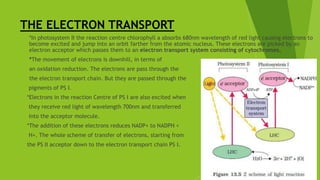
*Finally the NADP+ is reduced into NADPH+ and H+. This is called Z scheme.
*PS II supply electrons continuously by the splitting of water.
*The splitting of water is associated with the PS II. Water is split into H+ and
[o] electrons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/photosynthesis-170523040746/85/Photosynthesis-14-320.jpg)