Embed presentation
Download to read offline





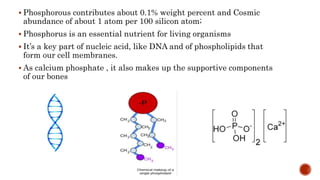


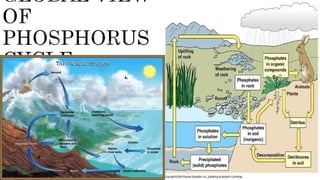












The document discusses the phosphorus cycle, which is essential for life. Phosphorus is limiting in many ecosystems and its cycle involves geological processes that move it between rocks, soil, organisms and ocean sediments over long timescales. The cycle has been impacted by human activities like mining, fertilizer use and transport, which are increasing phosphorus levels in waterways and causing eutrophication. This disrupts ecosystems and leads to issues like dead zones lacking in oxygen. Effectively managing phosphorus and reducing runoff can help address these problems.




















