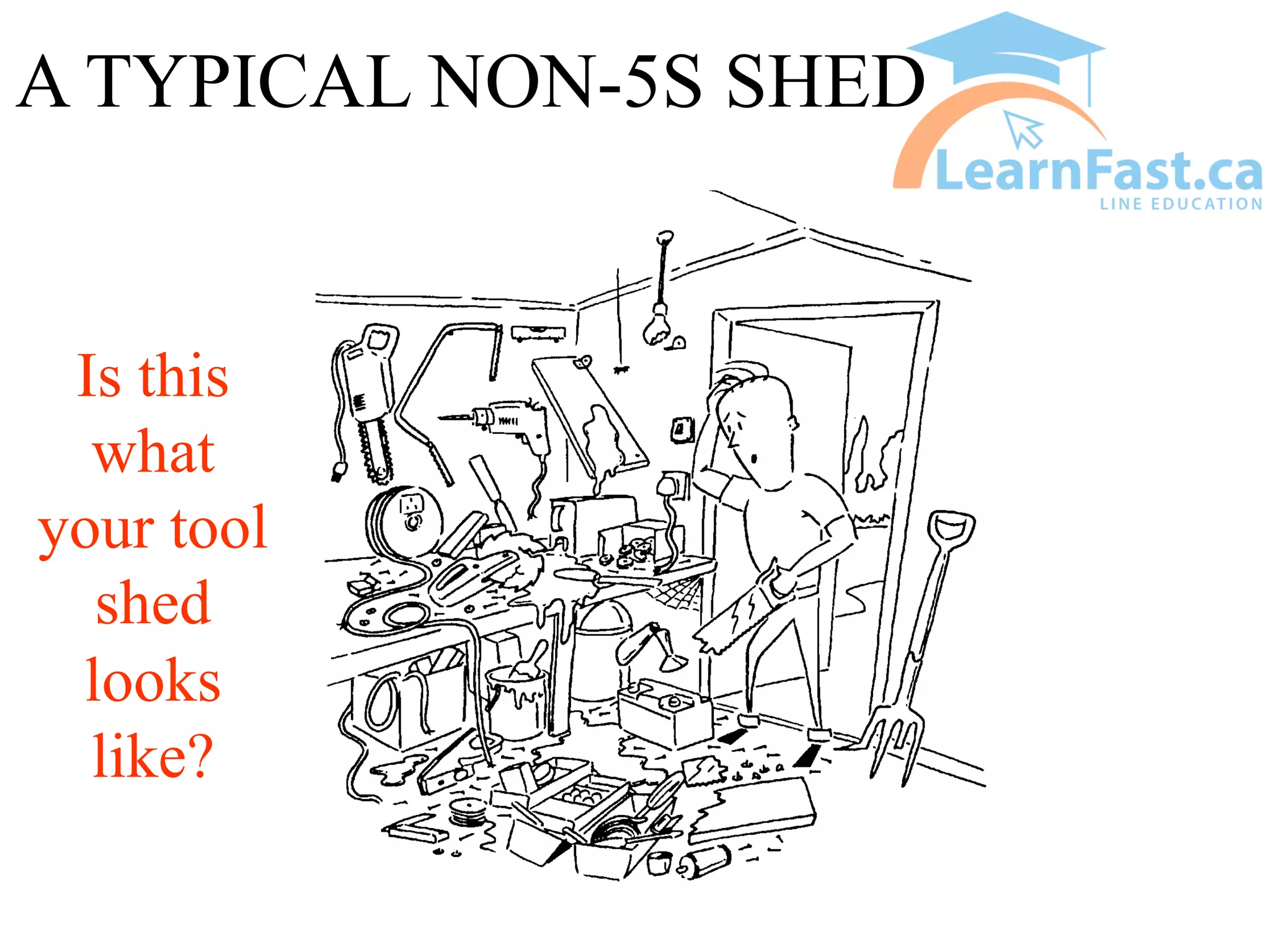
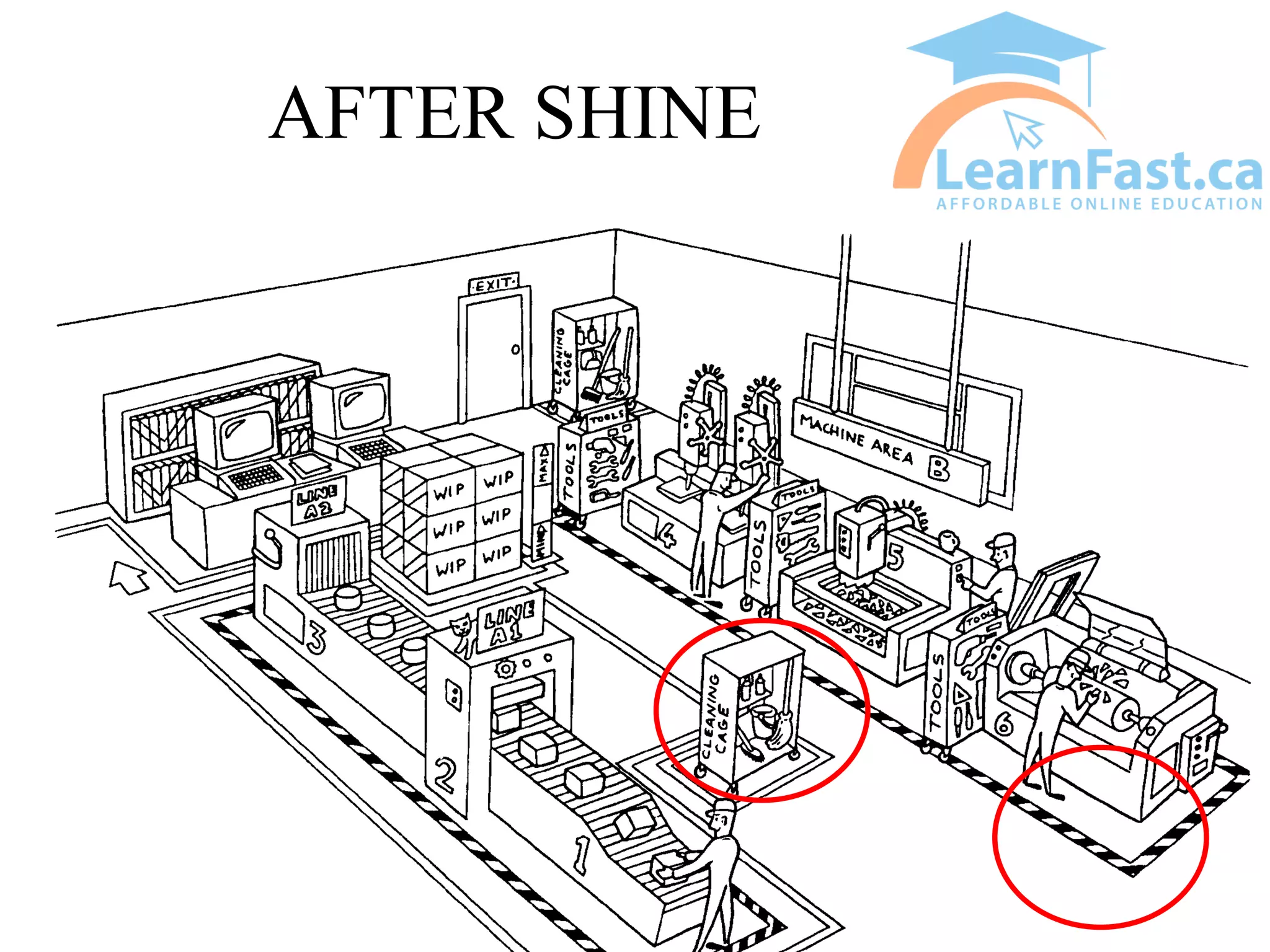
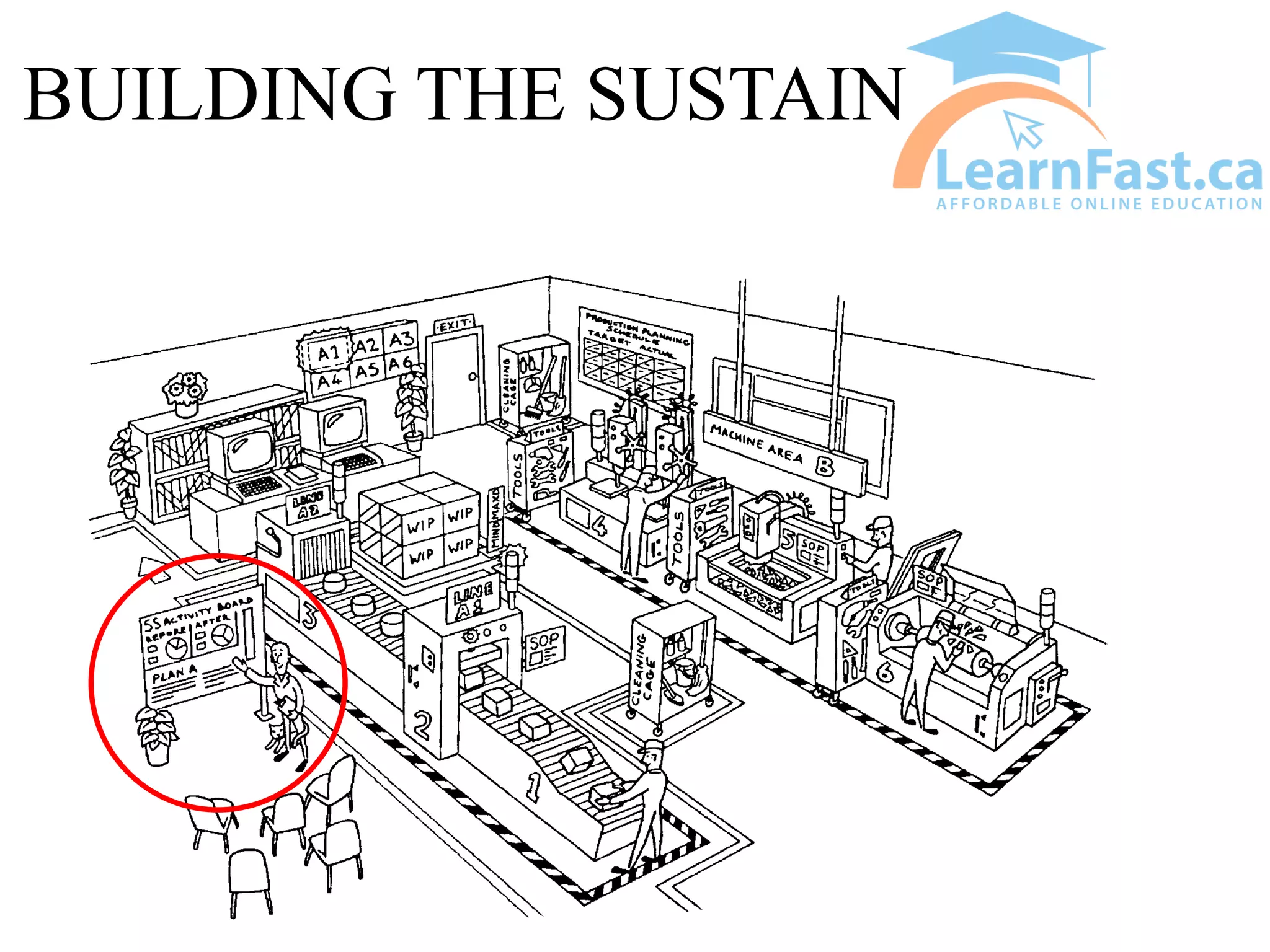
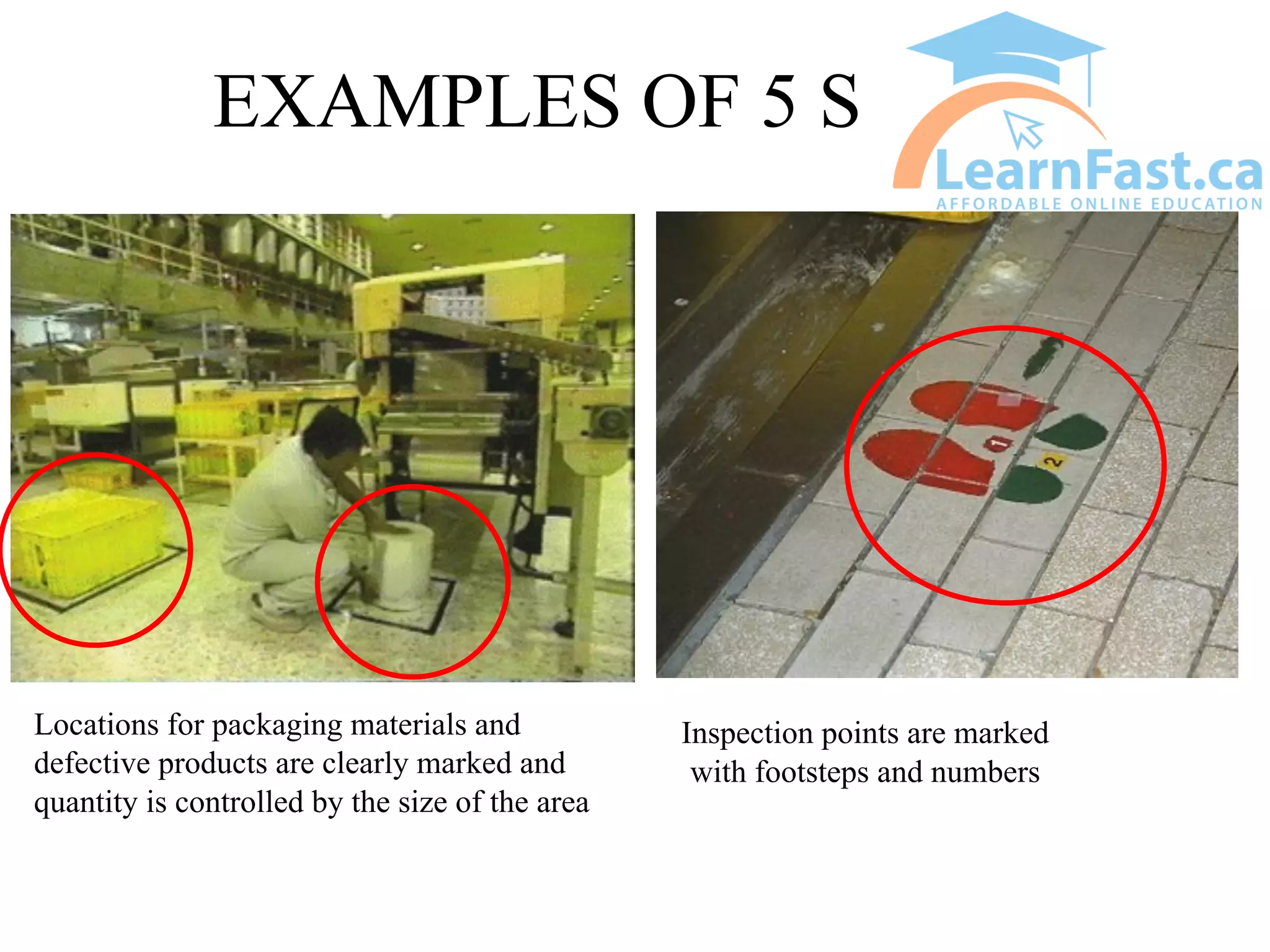
This document discusses the 5S methodology for organizing and standardizing a workspace. The 5S principles are Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. They involve removing unnecessary items, properly storing and labeling necessary items, cleaning the area, establishing standard work procedures, and sustaining the improvements. Examples show how applying 5S principles can transform disorganized areas like warehouses, tool sheds, production areas, and offices into clean, efficient workspaces where everything has a clear place and is easy to find.