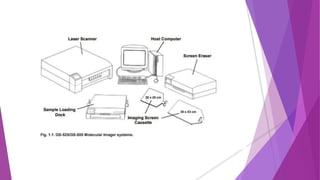
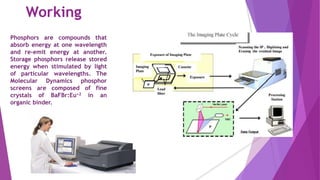
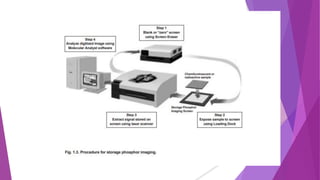
The document discusses a phosphorimager, which is an instrument that uses phosphor screens and laser scanning to detect and quantify radioactivity on samples like DNA, RNA, proteins, and tissues. It absorbs radiation from samples and stores the information as latent images on the phosphor screen. A laser then stimulates the screen to emit light proportional to the radioactivity, allowing the image to be captured digitally and analyzed. Phosphor imaging provides advantages over film methods like faster exposure times, greater sensitivity, and a wider dynamic range.