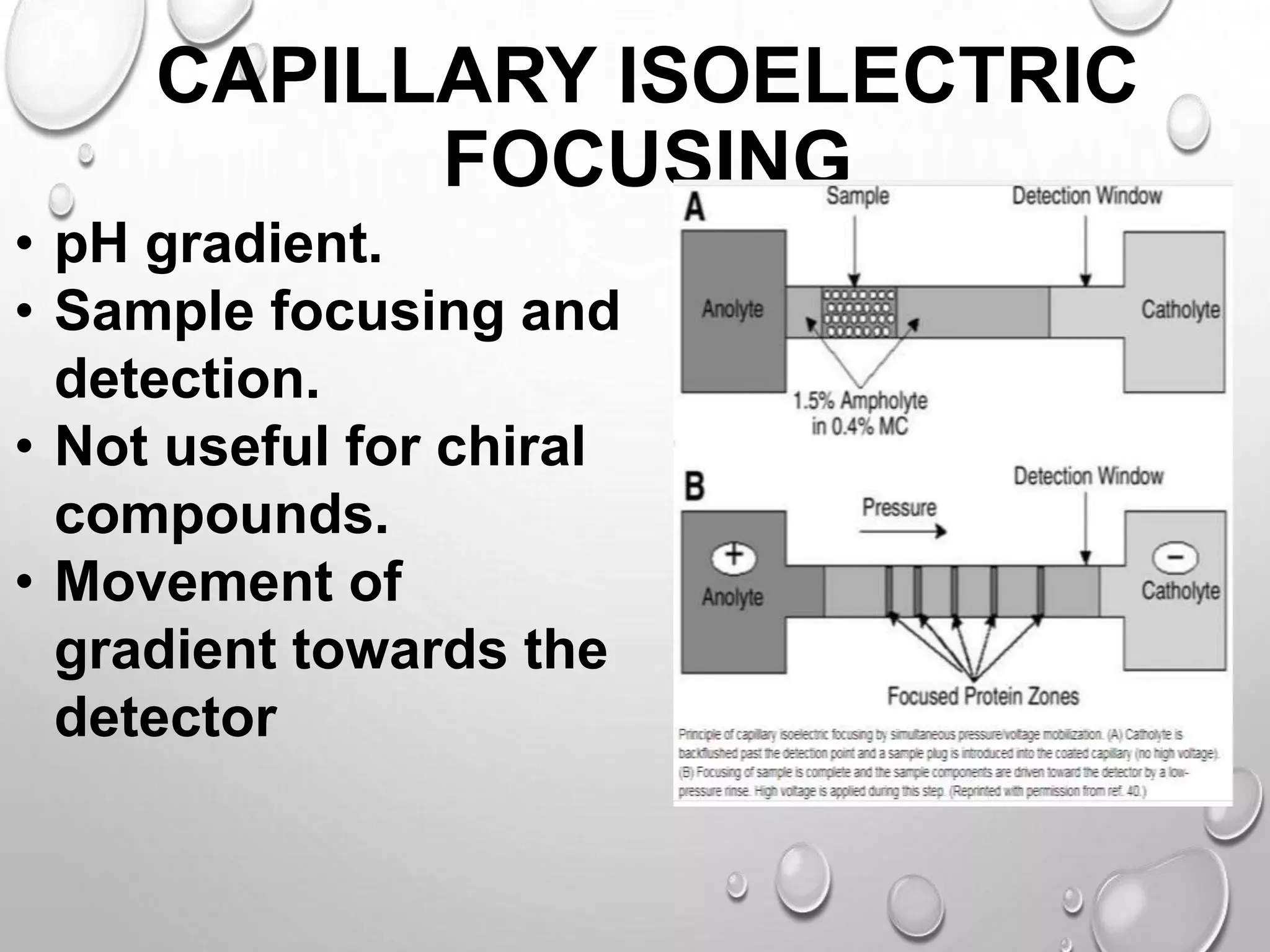
This document discusses isoelectric focusing, a technique used to separate proteins based on their isoelectric point (PI). Proteins are subjected to an electric field within a pH gradient, which causes them to migrate to the point in the gradient where their net charge is zero (their PI). Different proteins have different PIs and will therefore migrate to distinct positions in the gel. Isoelectric focusing provides high resolution separation and is useful for research applications such as taxonomy, cytology and immunology.