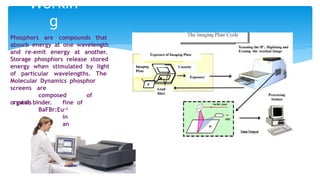
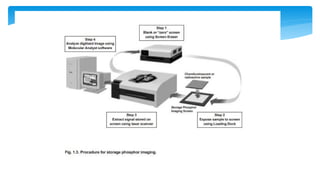
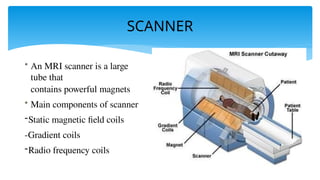
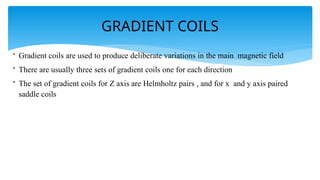
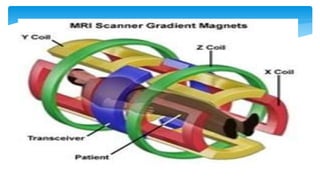
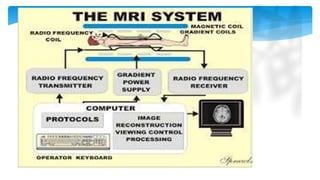
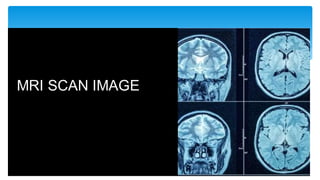
The document presents an assignment on imaging techniques, focusing on the phosphor imager and MRI technology. Phosphor imaging detects and quantifies radioactivity for various biological samples and offers advantages such as reduced exposure times and reusability compared to traditional methods. MRI uses magnetism and radio waves to produce detailed images of body structures, employing various components to create a magnetic field and analyze soft tissues, with practical applications in diagnosing numerous medical conditions.