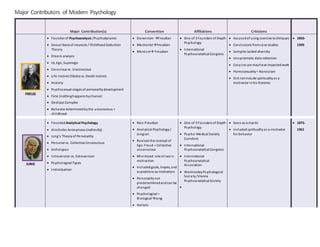
The document summarizes the major contributions and criticisms of several influential figures in modern psychology, including Freud, Jung, Adler, Horney, Maslow, Kohut, Klein, and Rogers. It outlines each psychologist's key theories and ideas, as well as their affiliations with different conventions and schools of thought. Some of the major criticisms highlighted include accusations of mysticism against Jung, disagreements with Horney's views on narcissism, and questions around Maslow's methodology and sample bias. The document provides an overview of the historical development of several approaches in modern psychology from Freudian psychoanalysis to humanistic and feminist perspectives.