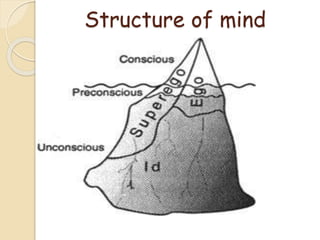
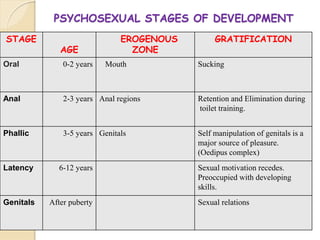
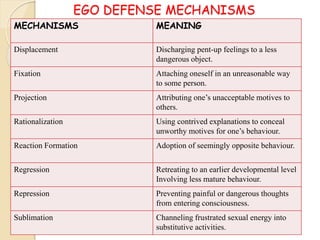
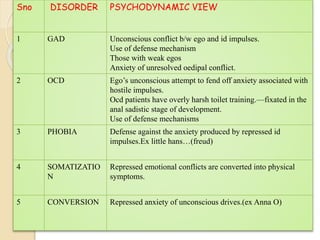
The psychodynamic approach views abnormal behavior as arising from unconscious psychological conflicts. Sigmund Freud developed psychodynamics and the structural model of the psyche, comprising the id, ego, and superego. The id operates on the pleasure principle, the ego balances id impulses with reality, and the superego incorporates moral standards. Psychodynamics examines how early experiences and defense mechanisms shape personality development through Freud's psychosexual stages. Various disorders like anxiety and OCD result from fixations or failures to resolve conflicts between the structures of the psyche.