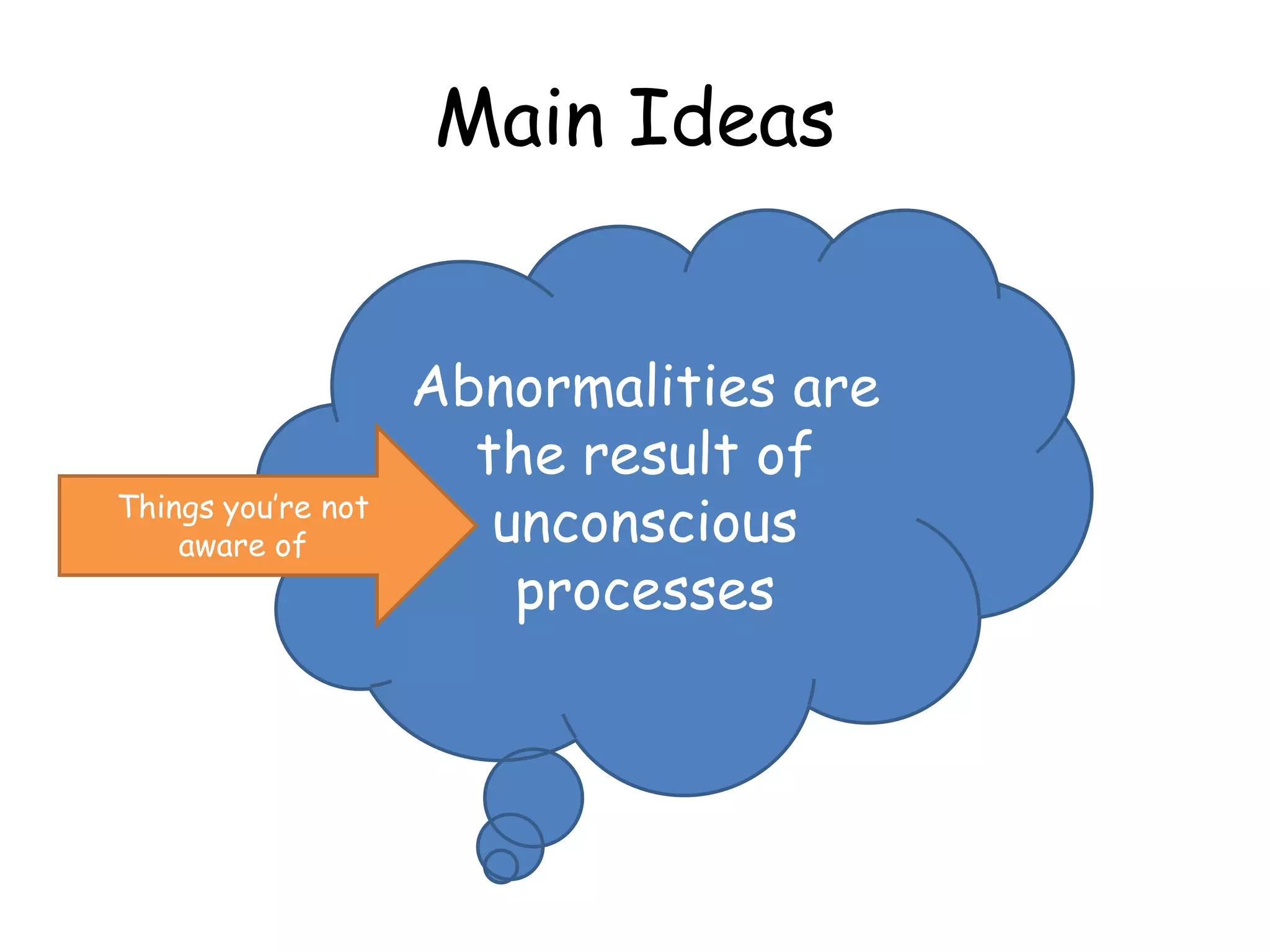
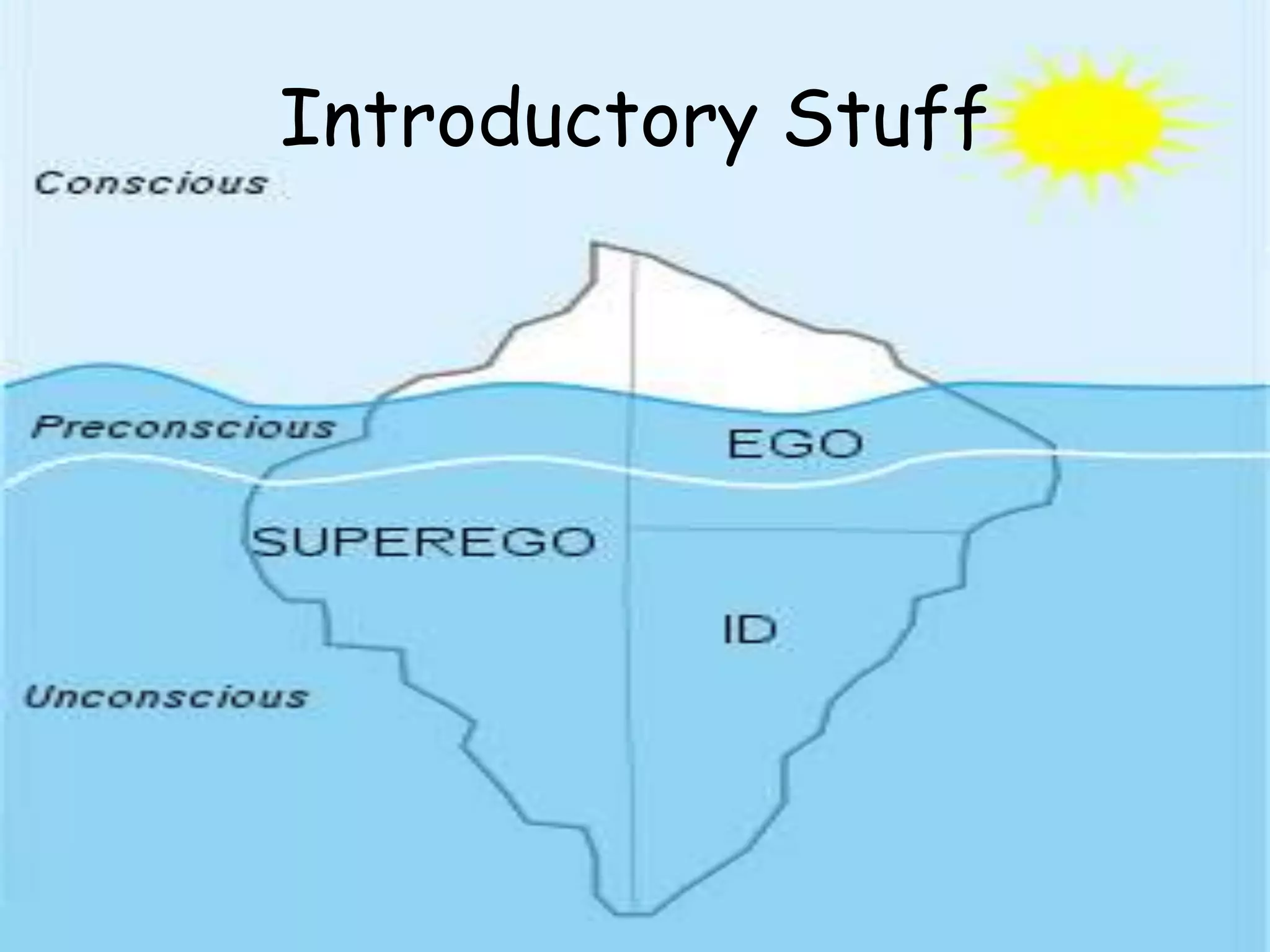
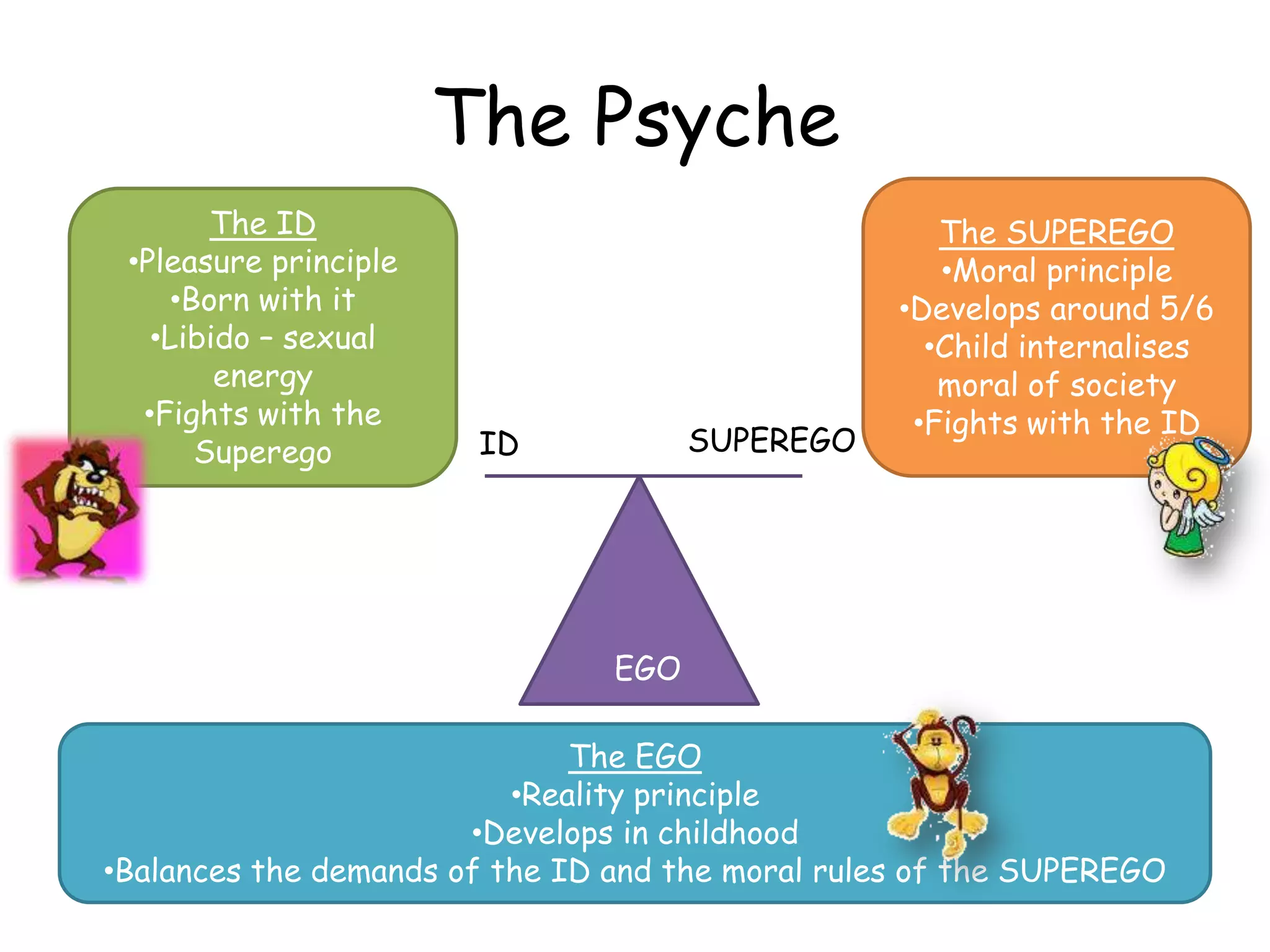
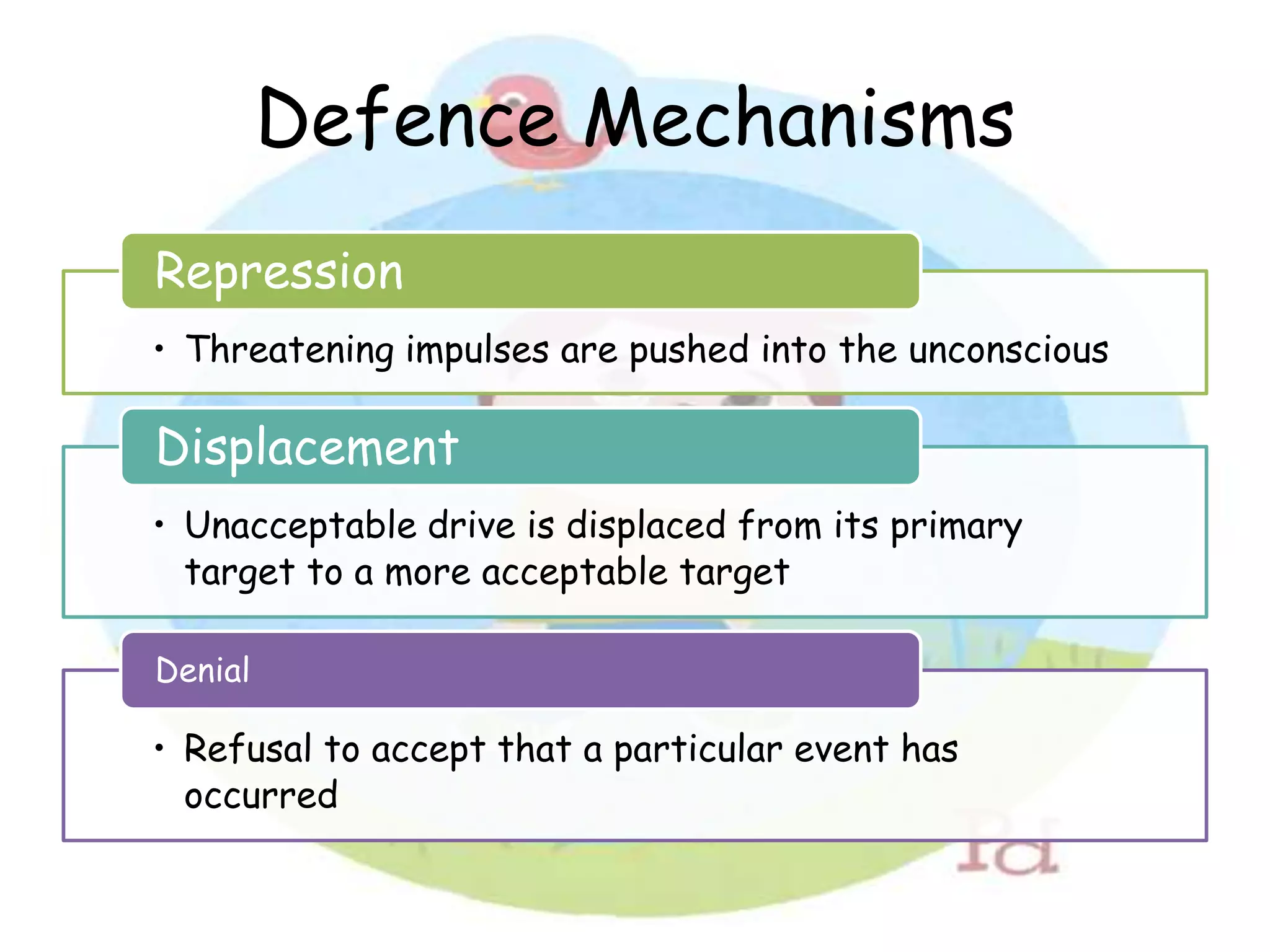
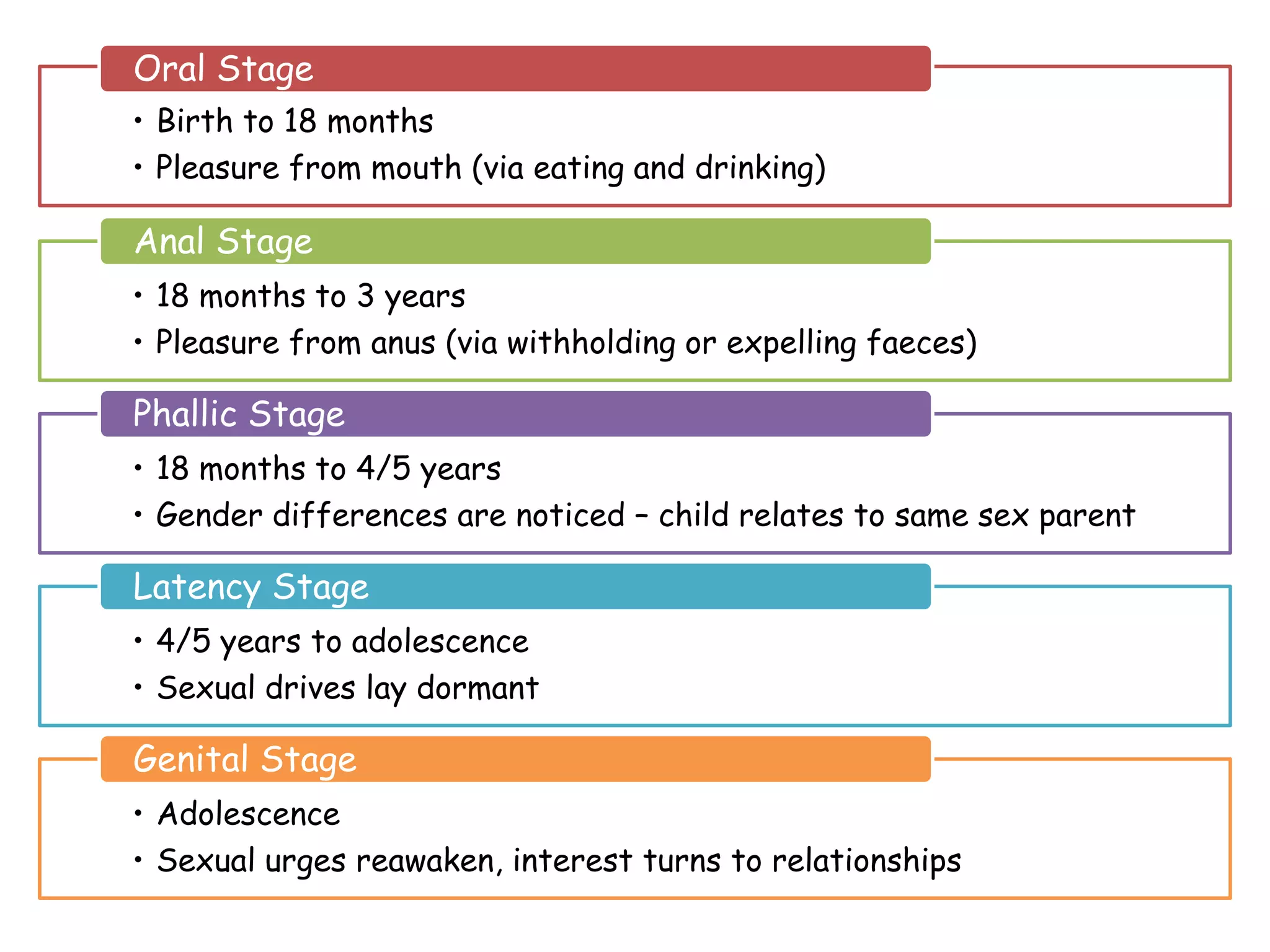
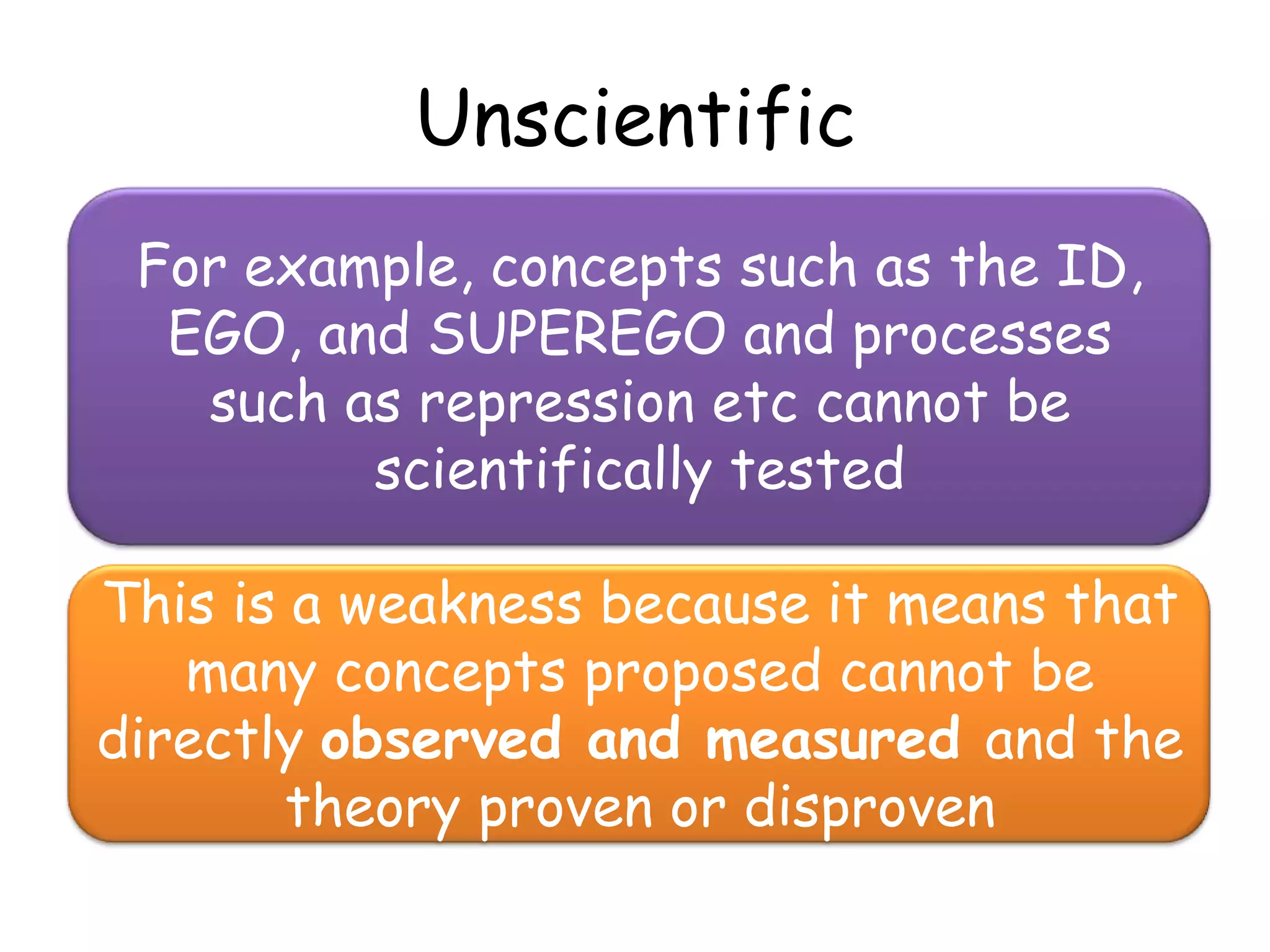
Freud's psychodynamic approach views abnormalities as arising from unconscious processes and intrapsychic conflicts between the id, ego, and superego. It proposes that fixation during psychosexual development stages like oral or anal can lead to disorders if a child is under or over gratified. Defence mechanisms like repression may form if conflicts cause anxiety, but if unsuccessful disorders may develop. While influential, weaknesses include its determinism, reductionism, and lack of scientific testability of concepts like the psyche's structures.