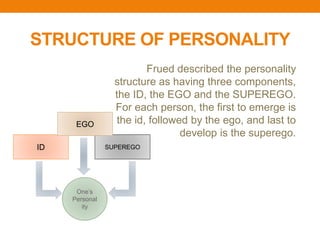
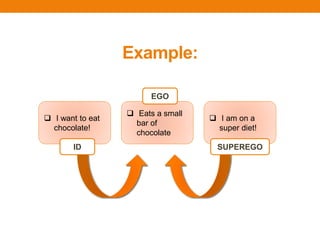
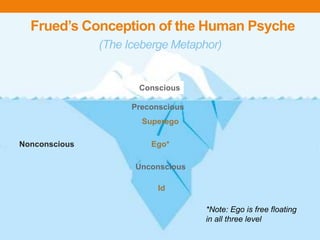
Sigmund Freud developed psychoanalytic theory and focused on the unconscious mind. He believed human behavior is determined by unconscious motivations like pleasure/pain. Freud described psychosexual development through oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital stages. Fixation in a stage can result in personality traits. He also described the id, ego, and superego structures of personality and the topographical model of the conscious, preconscious, and unconscious minds.