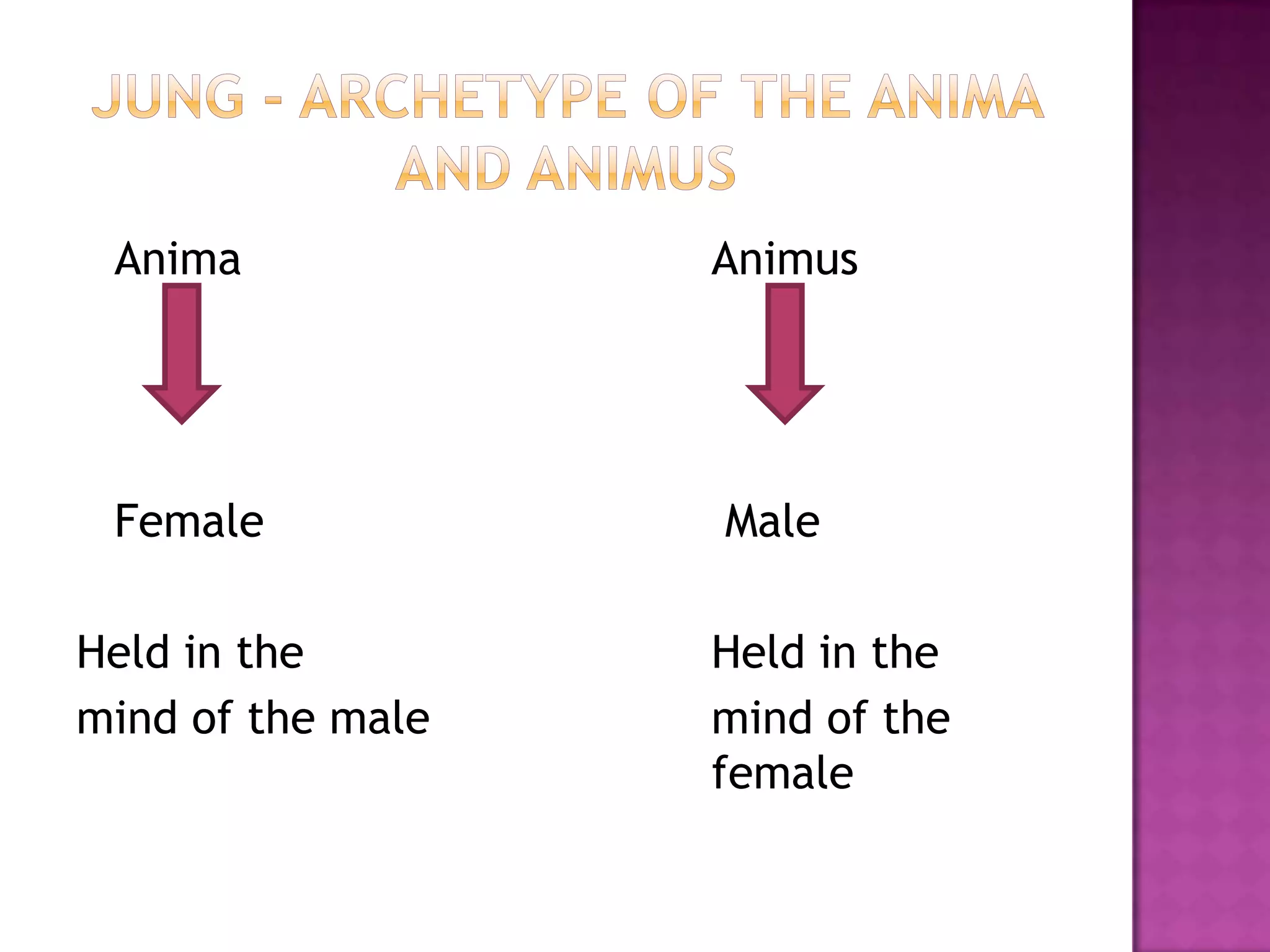
This chapter discusses several neo-Freudian theorists and their expansions on Freudian psychoanalysis. Alfred Adler focused on social interest and the striving for superiority. Erik Erikson described 8 stages of psychosocial development and the importance of establishing identity. Karen Horney discussed psychological health and neurosis as well as three interacting styles of relating to others. Carl Jung disagreed with Freud on aspects like the life force and focused more on spirituality and archetypes in the collective unconscious like the anima/animus and persona. Jung also described personality types of introversion/extroversion and ways of thinking like sensation and intuition.