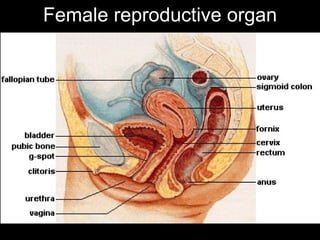
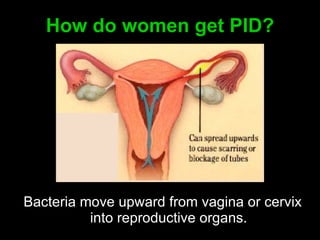
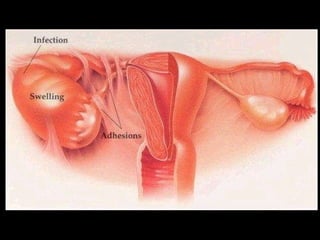
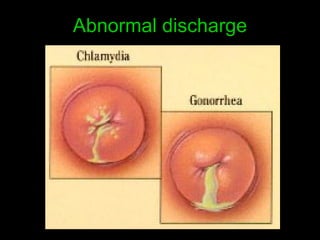
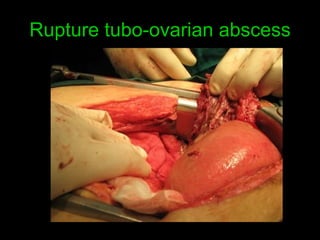
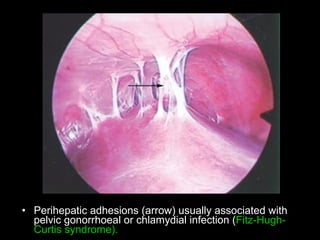
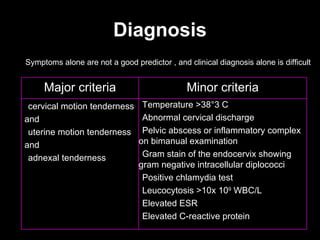
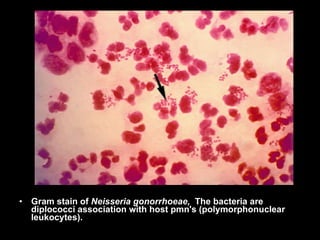
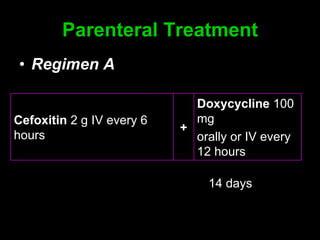
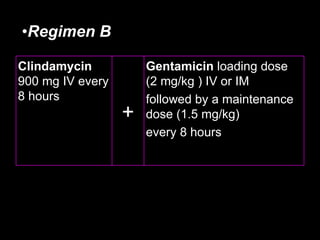
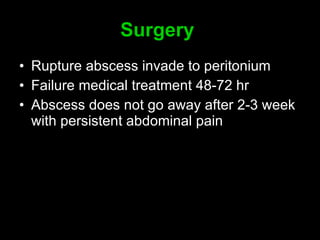
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It is commonly caused by bacteria like Chlamydia and gonorrhea spreading from the vagina or cervix. Symptoms include lower abdominal pain and bleeding between periods. Without treatment, PID can lead to long-term complications such as infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Treatment involves antibiotics, sometimes administered intravenously in severe cases. Prevention focuses on screening and treatment of sexually transmitted infections.