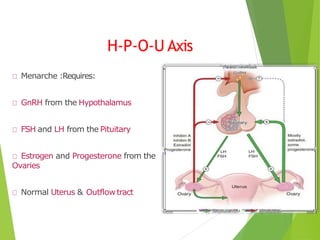
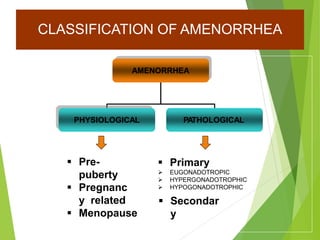
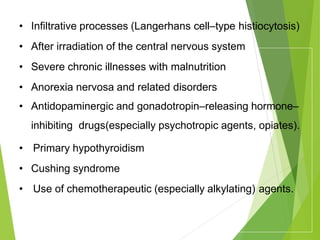
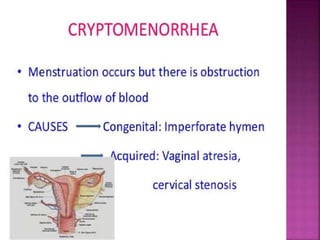
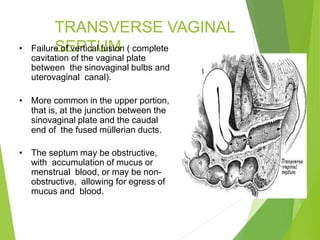
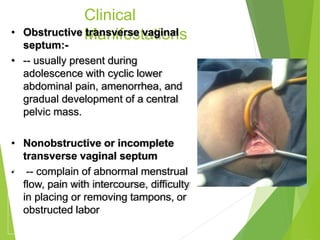
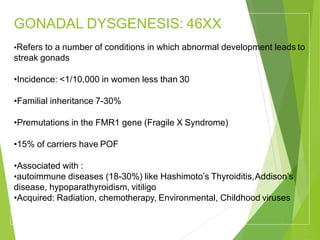
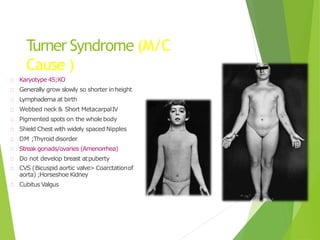
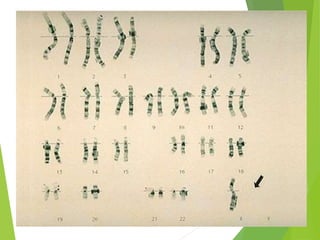
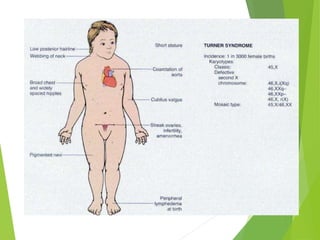
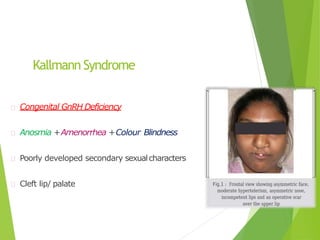
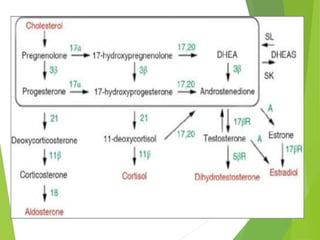
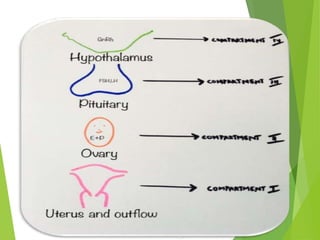
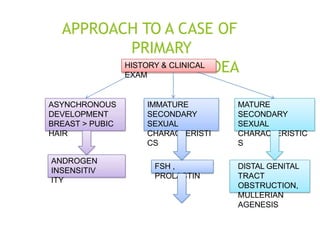
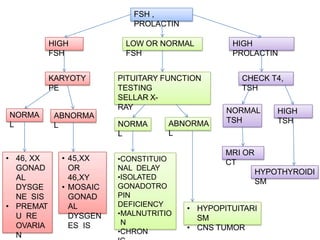
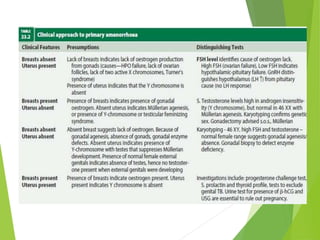
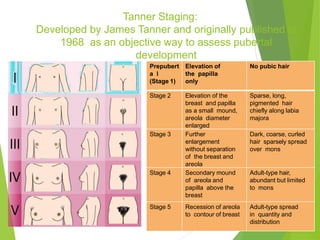
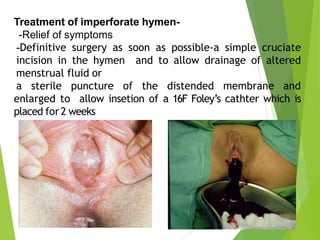
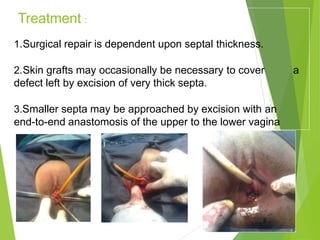
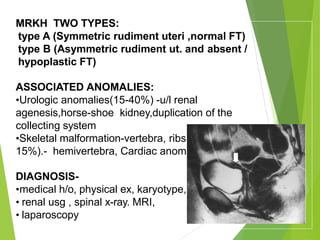
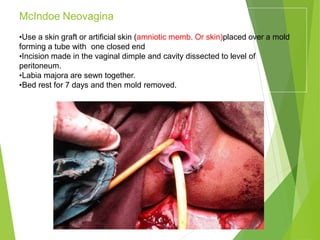
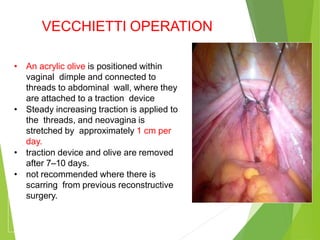
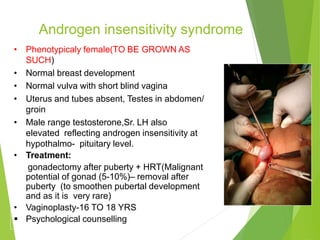
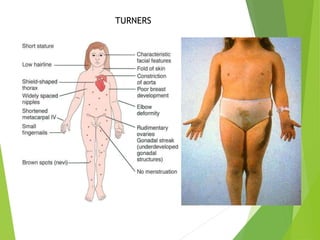
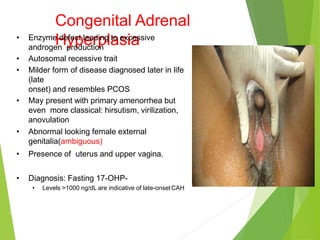
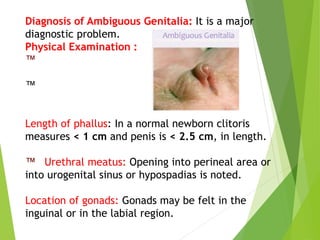
Primary amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstruation. It can be caused by physiological or pathological factors. A thorough evaluation includes obtaining a medical history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests. The history aims to understand pubertal development and identify potential causes like genetic conditions, while the exam evaluates secondary sexual characteristics and external genitalia. Key tests involve hormonal profiles to classify amenorrhea as eugonadotropic, hypergonadotropic, or hypogonadotropic. Further tests like ultrasound, MRI and karyotyping help diagnose conditions like Müllerian agenesis or Turner syndrome. The goal is to understand the underlying pathology and provide appropriate treatment.