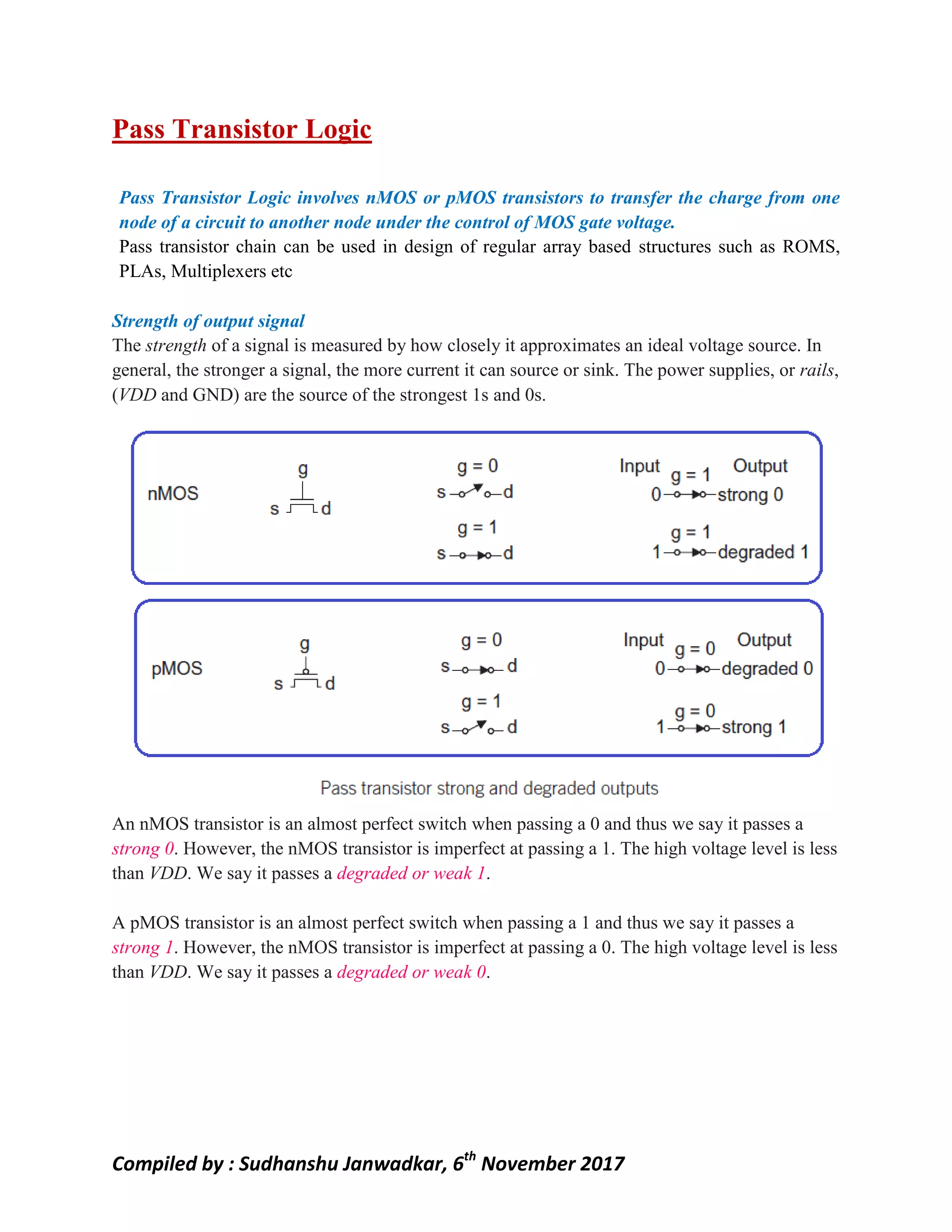
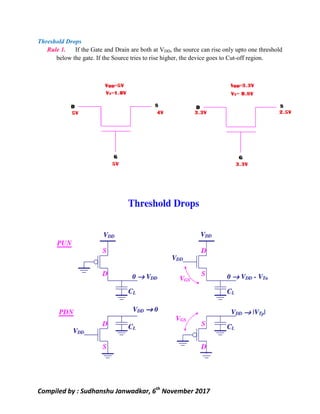
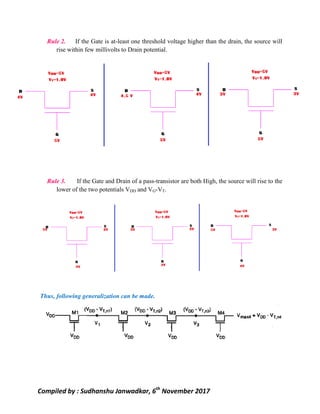
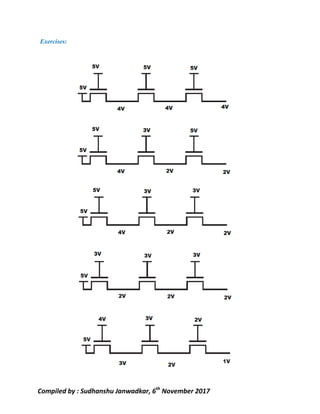
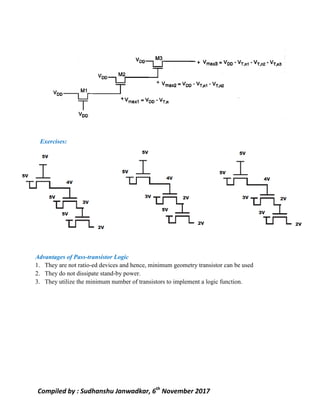
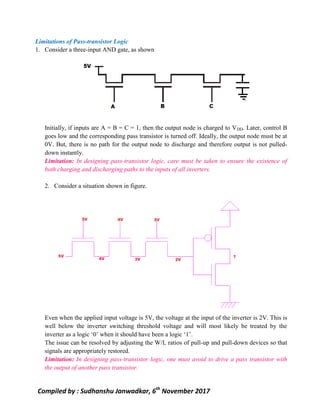
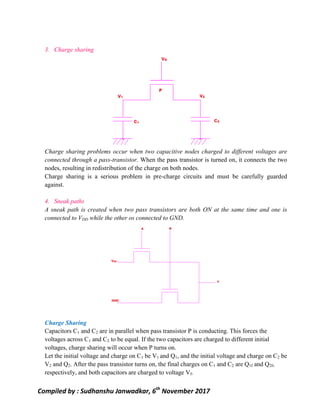
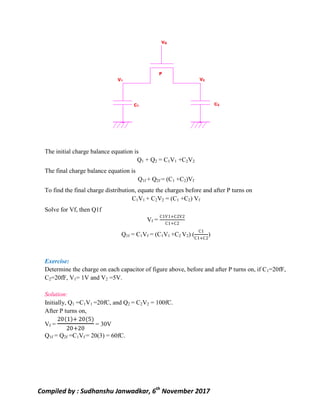
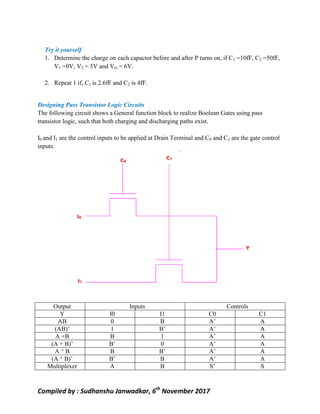
This document discusses pass transistor logic, which uses MOS transistors to transfer charge between circuit nodes under gate control. It describes how nMOS and pMOS transistors can pass strong or weak signals depending on their configuration. Threshold voltage drops, charge sharing problems, and sneak paths that can occur in pass transistor logic circuits are also covered. The document provides examples of analyzing charge distribution before and after transistors turn on, and presents a general design for pass transistor logic gates that ensures both charging and discharging paths exist. Exercises are included on analyzing charge sharing and designing pass transistor logic circuits like majority gates and decoders.