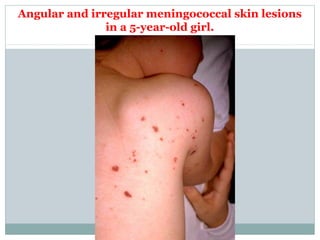
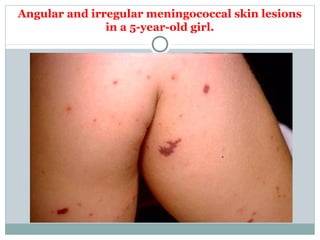
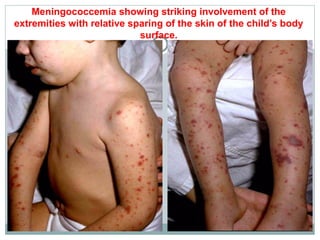
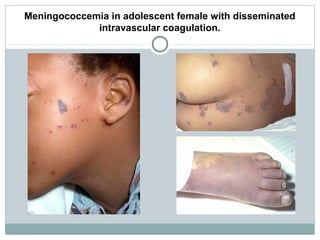
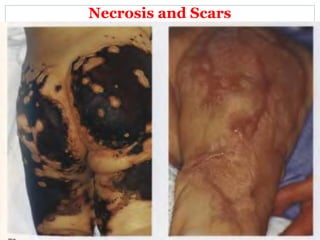
This document provides information on meningococcal infection. It begins by defining meningococcal infection and describing its causative agent, Neisseria meningitidis. It then covers the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical forms, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of meningococcal infection. Key points include that it is transmitted via air droplets and can cause meningitis, meningococcemia, or both. Clinical features depend on the form but may include fever, rash, headache and vomiting. Diagnosis involves examining cerebrospinal fluid which shows pleocytosis. Meningococcal infection is a serious public health issue worldwide.