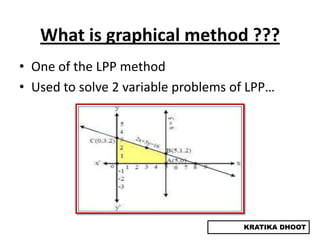
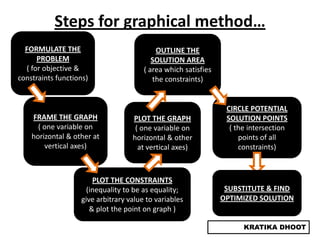
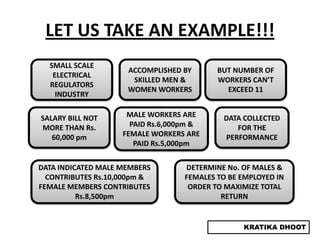
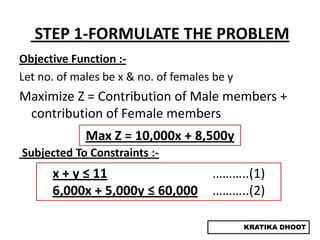
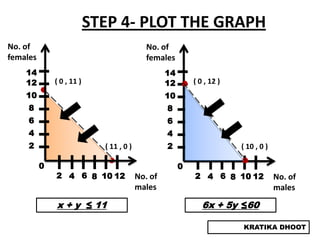
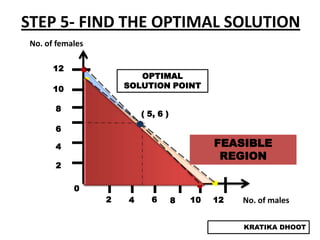
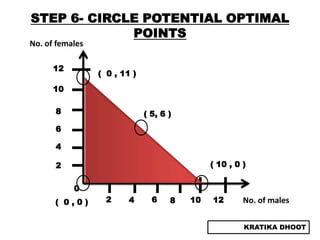
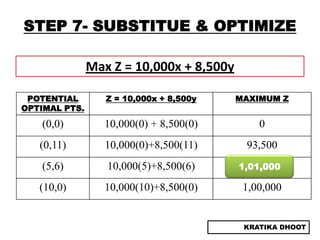
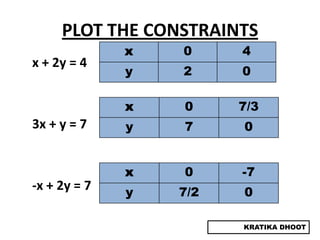
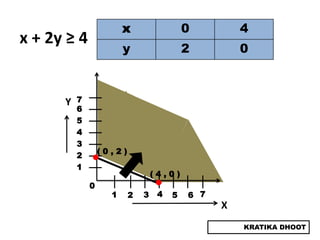
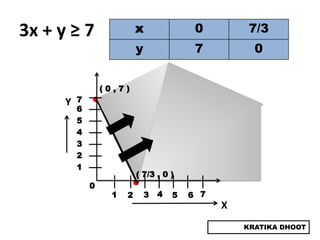
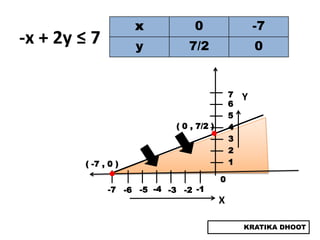
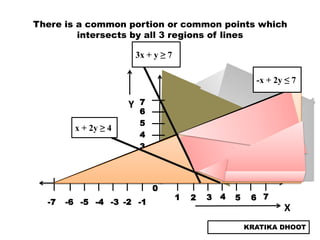
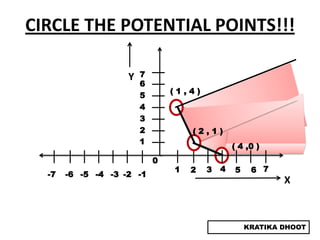
The document provides a summary of a presentation on solving linear programming problems (LPP) using the graphical method. It defines LPP and the graphical method. It then walks through the steps to solve an example LPP problem graphically, including formulating the problem, framing the graph, plotting the constraints, finding the optimal solution point, and determining the maximum value. The summary concludes that the optimal solution for the example problem is 5 male workers and 6 female workers, with a maximum total return of Rs. 1,01,000.