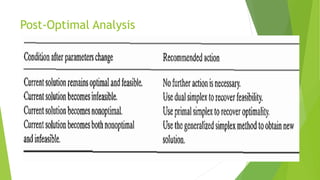
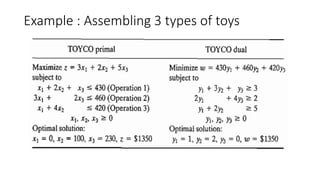
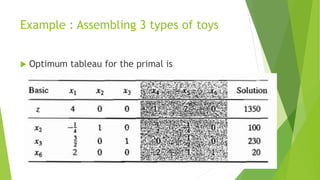
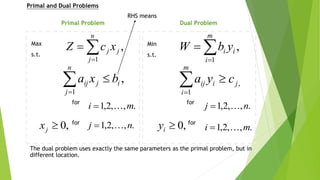
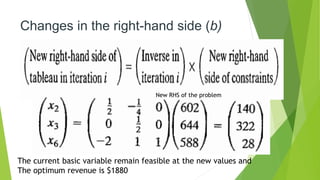
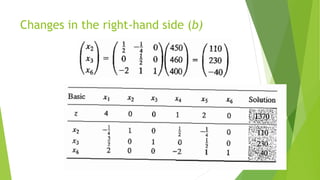
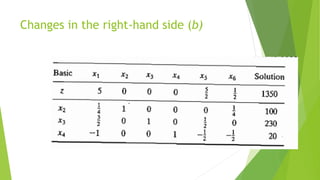
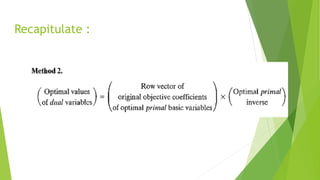
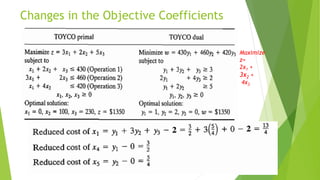
The document discusses post-optimal analysis in linear optimization problems. It describes how changes can affect feasibility or optimality, including changes to right-hand sides, adding new constraints, or changing objective coefficients. It also discusses adding a new activity/variable and using the dual simplex method to find the new optimal solution.