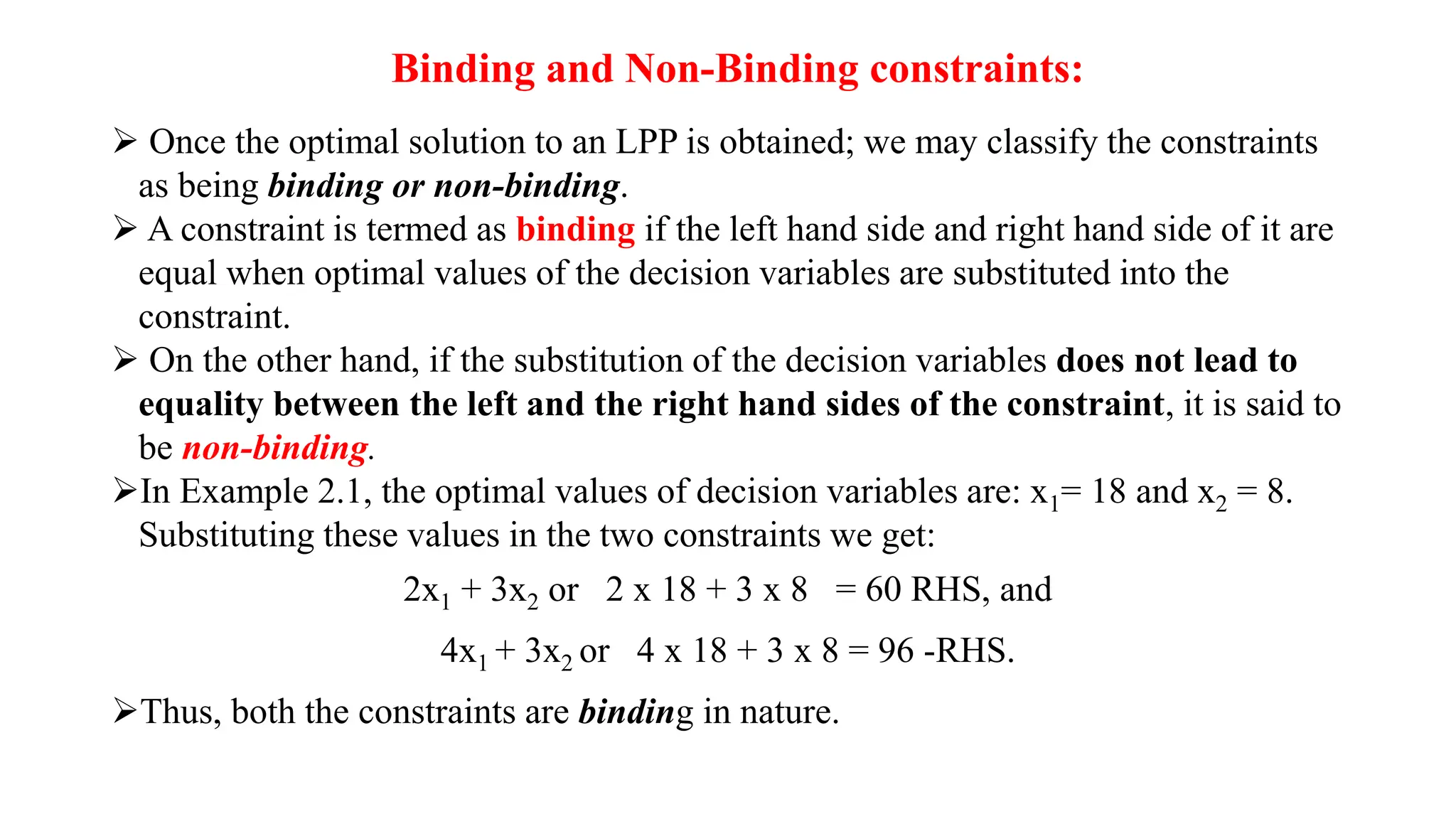
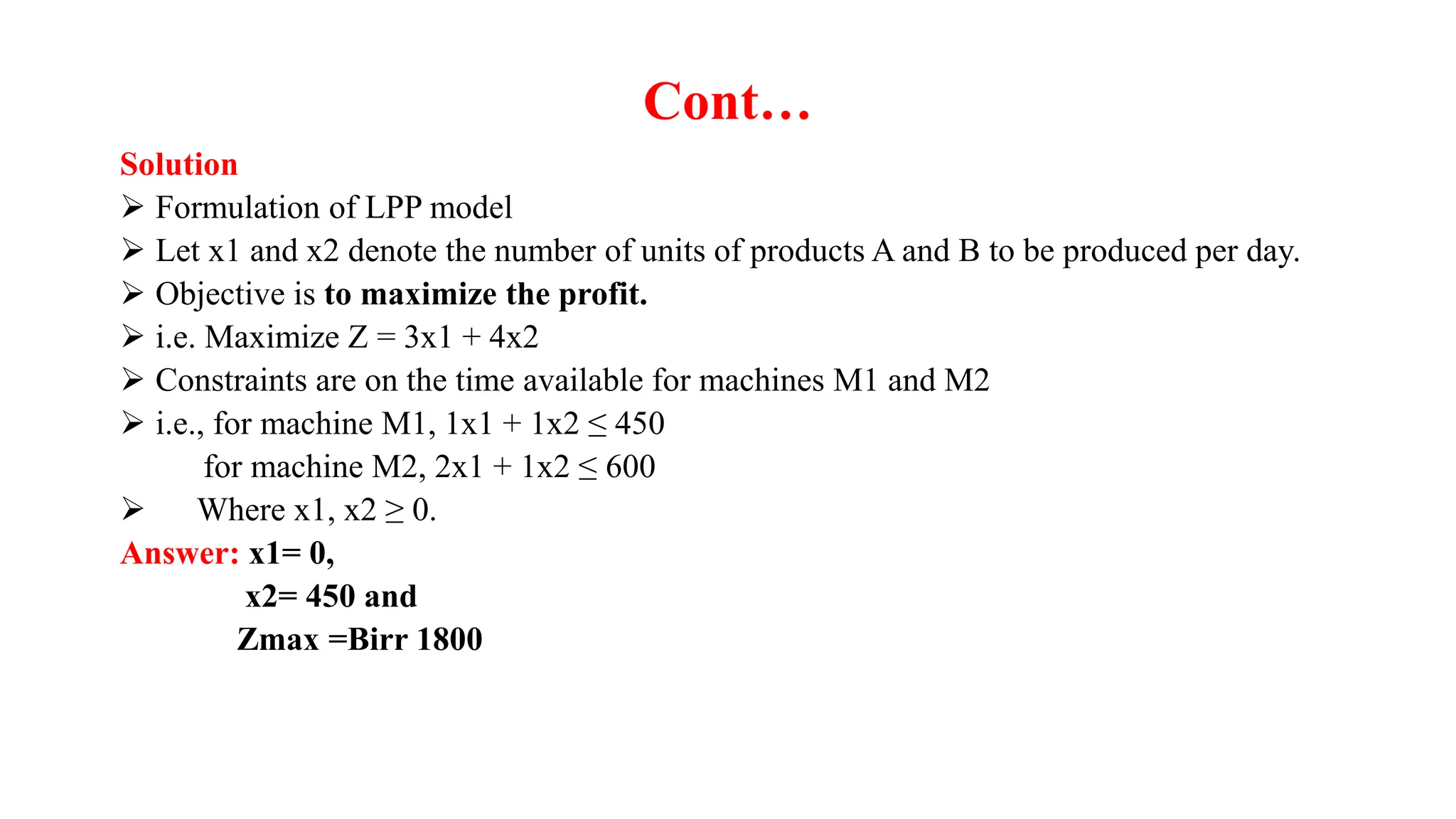
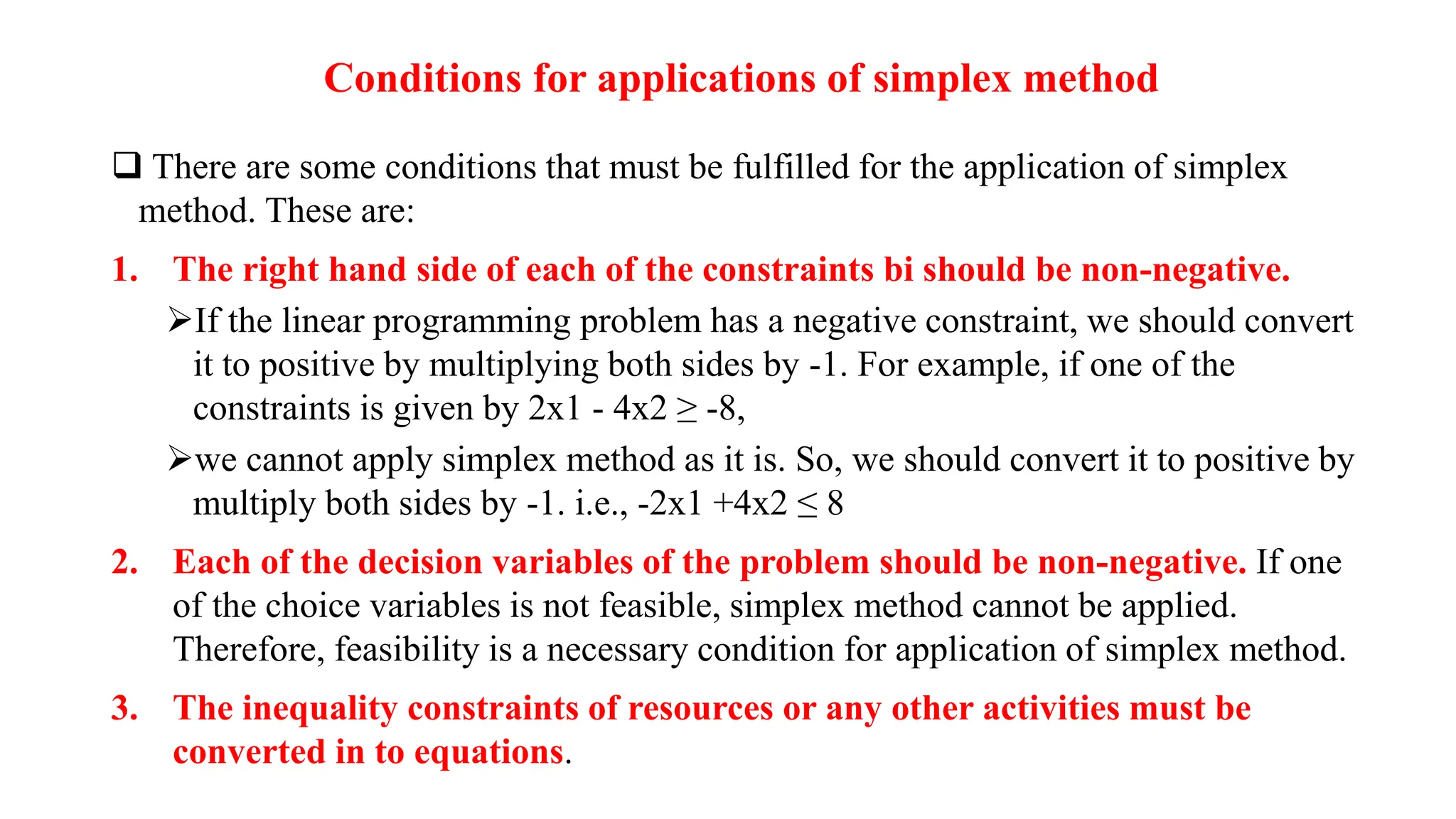
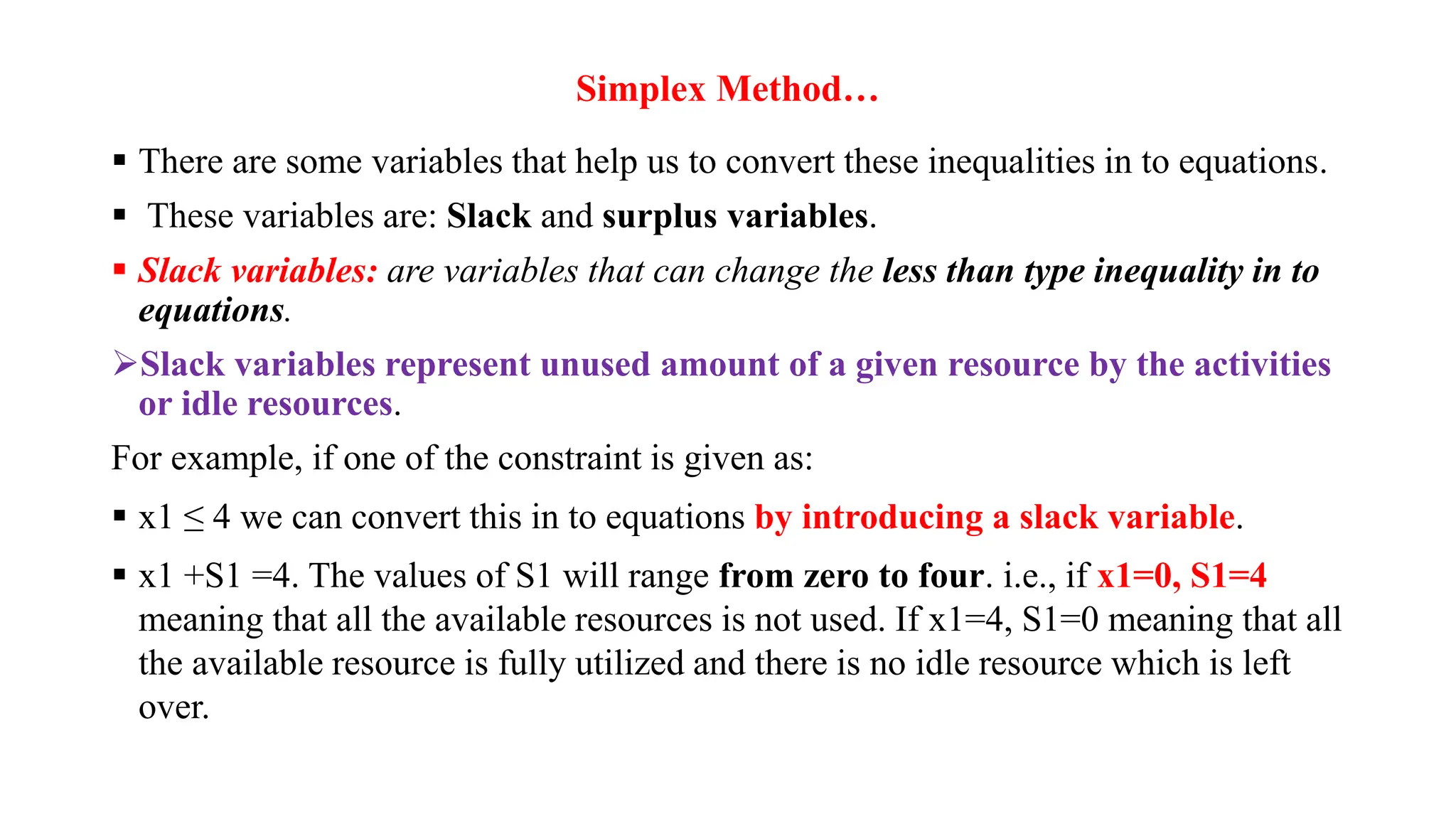
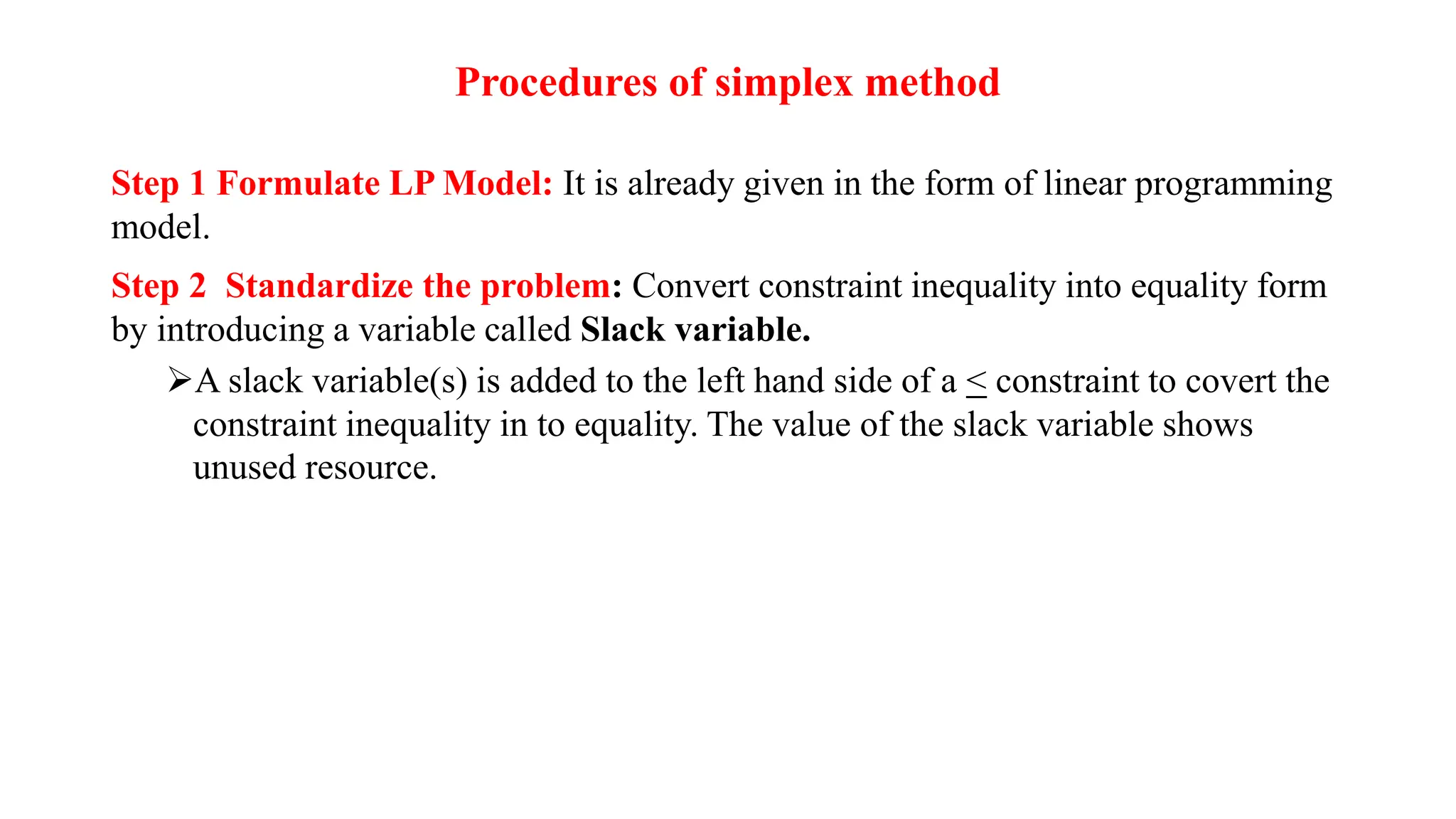
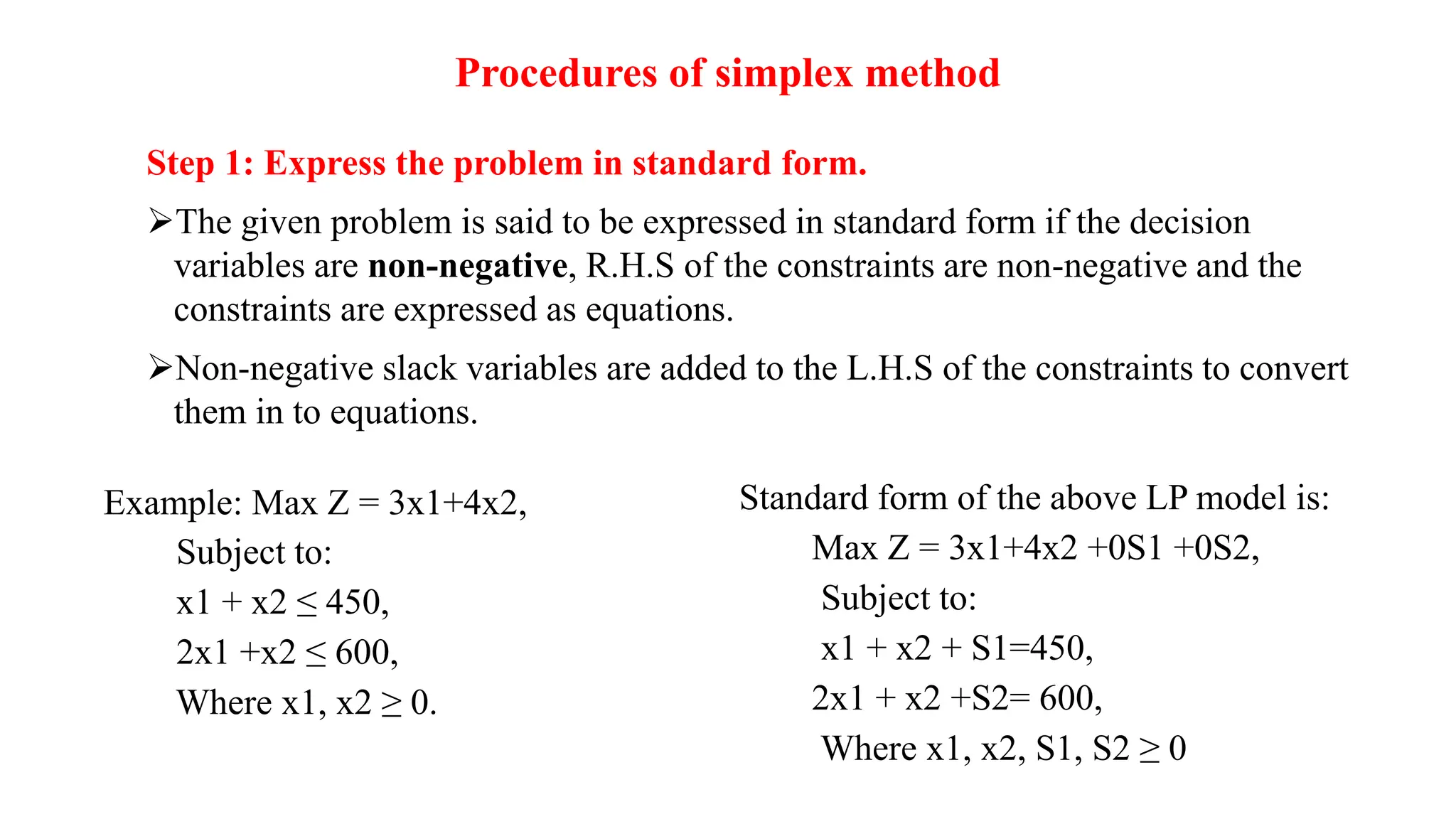
There are three special cases of linear programming problems:
1. Multiple optimal solutions - When the objective function represents a line parallel to an edge of the bounded feasible region, resulting in more than one optimal solution.
2. Unbounded solution - When the feasible region is unbounded in at least one direction, meaning the decision variables can increase infinitely without violating constraints.
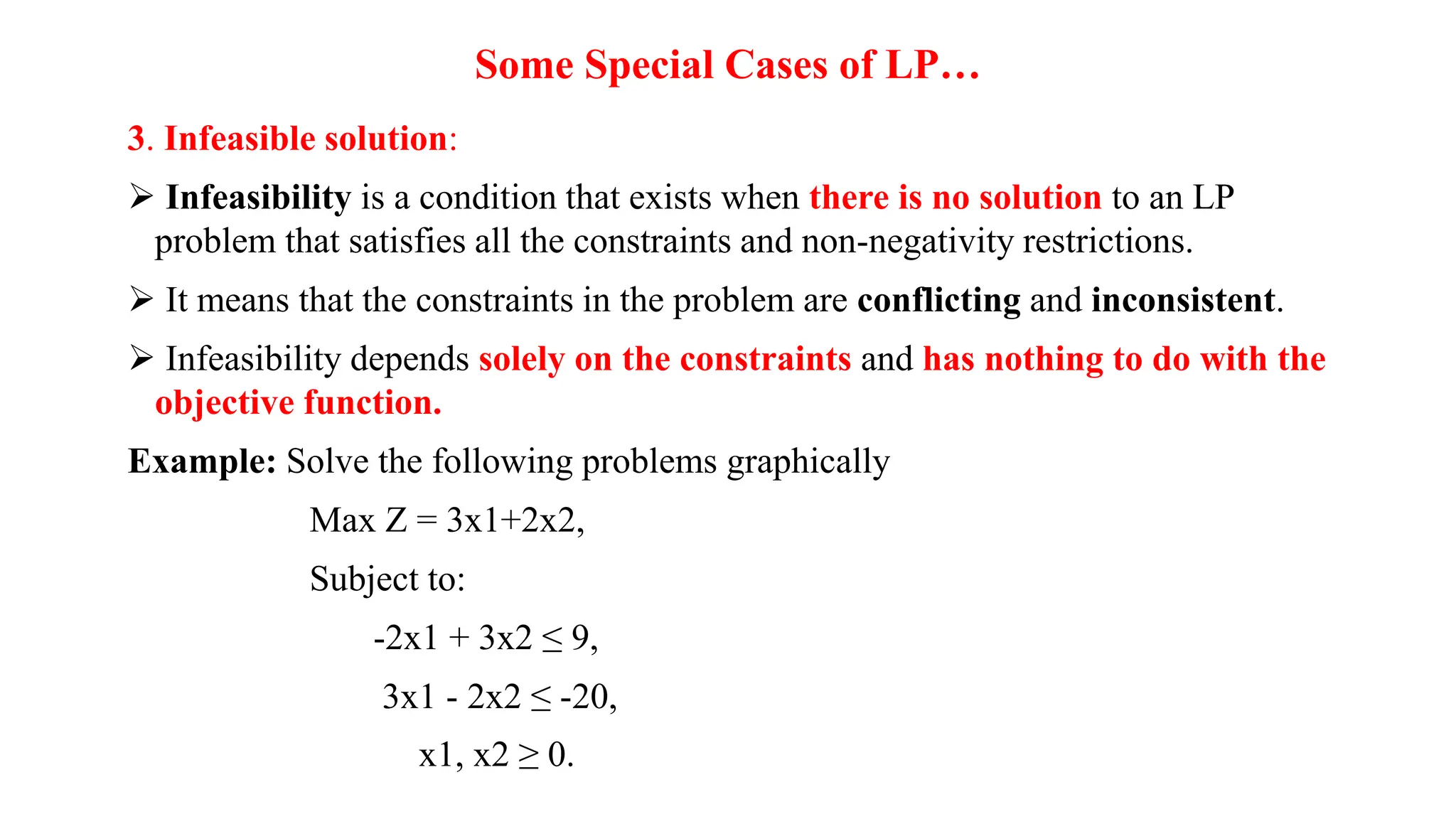
3. Infeasible solution - When the constraints are conflicting and there is no feasible solution that satisfies all constraints and non-negativity conditions.