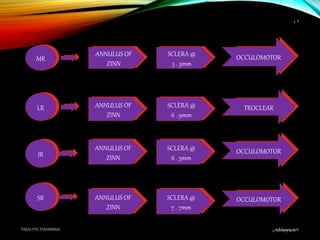
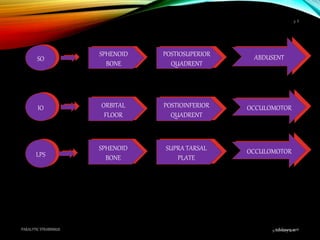
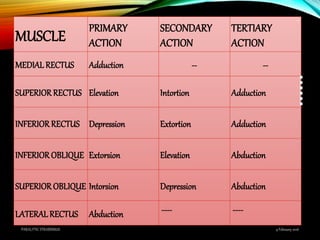
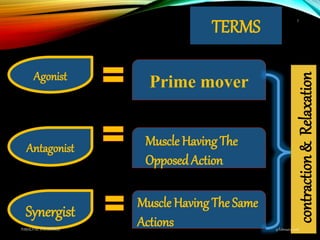
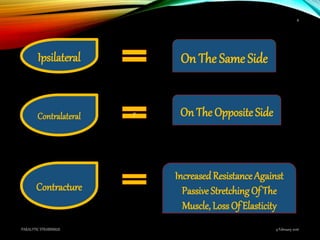
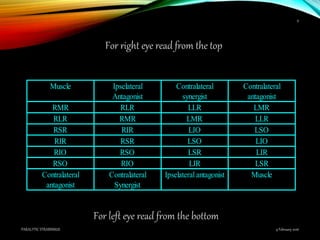
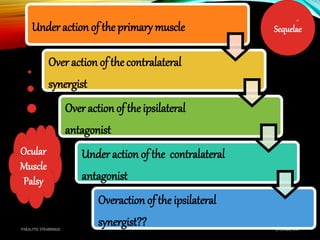
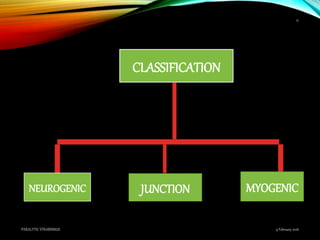
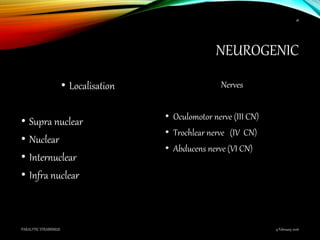
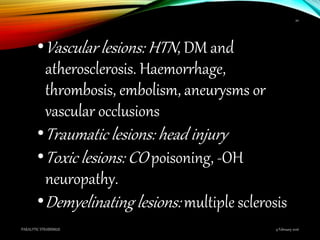
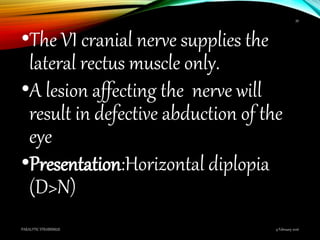
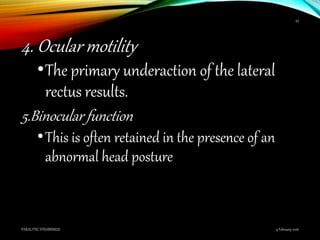
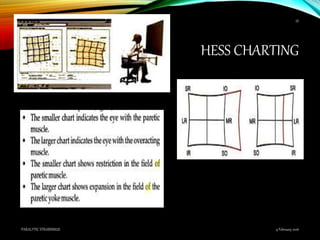
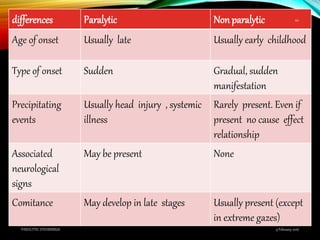
Paralytic strabismus is caused by motor deficiency of one or more extraocular muscles due to neurogenic, myogenic or junctional disorders. Common types include third, fourth and sixth nerve palsies which result in limited eye movements and misalignment. Third nerve palsy affects elevation, adduction and depression while fourth and sixth nerve palsies impact specific individual muscles. Investigation involves assessment of eye alignment, movements, diplopia and visual acuity to localize the lesion. Management depends on severity but may include occlusion therapy, prisms or strabismus surgery.