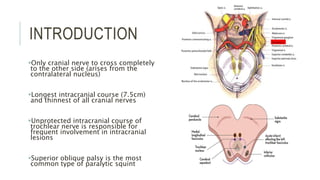
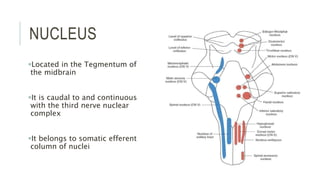
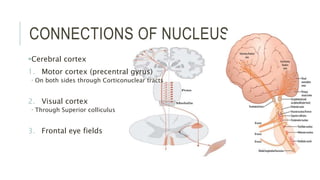
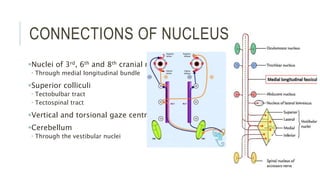
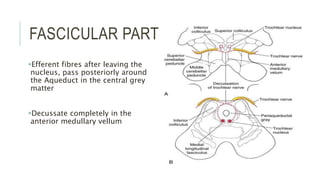
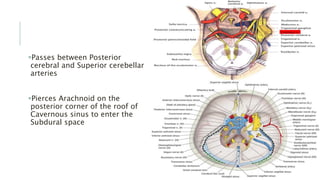
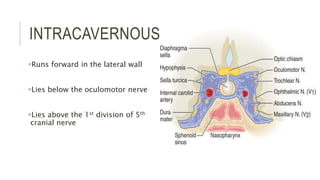
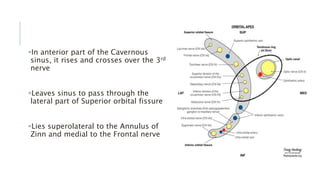
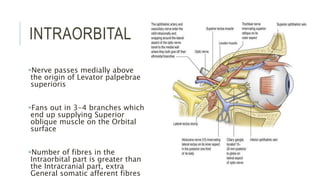
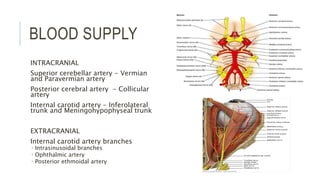
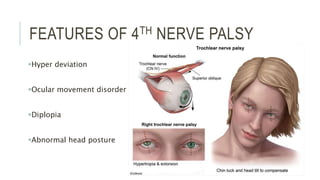
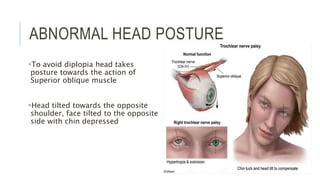
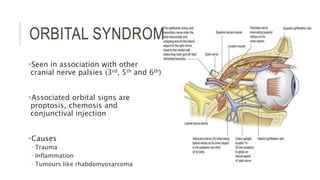
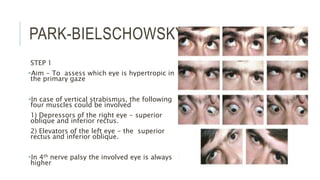
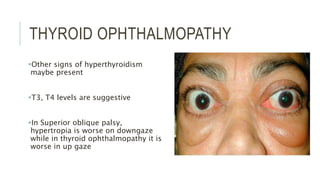
This document provides an overview of the trochlear nerve (cranial nerve IV), which innervates the superior oblique eye muscle. It discusses the anatomy and course of the nerve from its nucleus in the midbrain through the skull and orbit. Key points include that the trochlear nerve is the only cranial nerve to decussate and has the longest intracranial course. Causes of trochlear nerve palsy include congenital issues, trauma, vascular problems, and tumors. Clinical features of trochlear nerve palsy are hyperdeviation of the eye, limited eye movements, diplopia, and abnormal head posture. The document also outlines tests to diagnose trochlear nerve pals