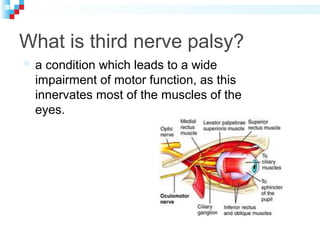
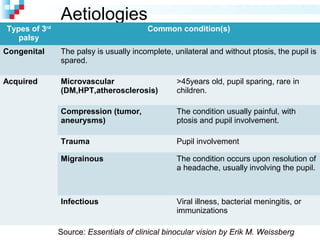
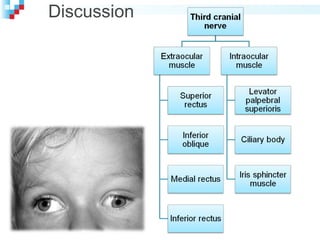
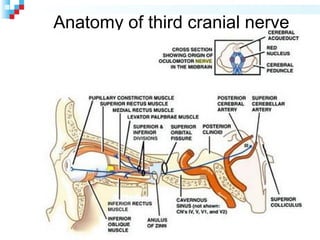
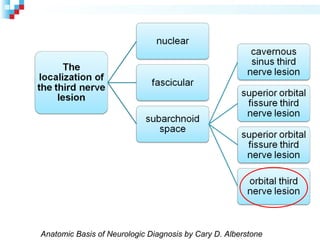
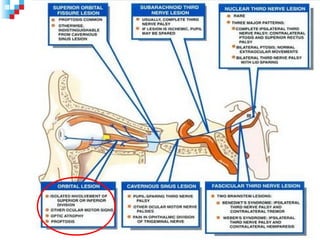
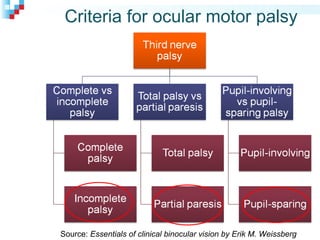
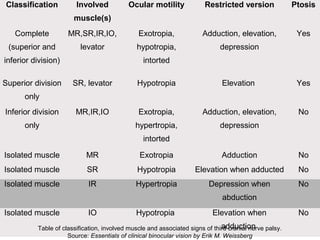
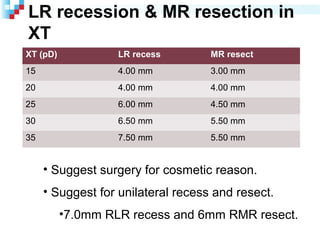
Third nerve palsy is a condition that leads to impairment of motor function as the third cranial nerve innervates most eye muscles. It can be congenital or acquired through conditions like diabetes, hypertension, tumors or trauma. Acquired third nerve palsy often involves patients over 45 and can cause ptosis and pupil involvement while congenital palsy is usually unilateral and incomplete without ptosis. The document discusses a case study of a 18-year old female referred for assessment of right eye exotropia secondary to trauma as a child. Her examination findings and diagnosis of right eye exotropia are presented along with a management plan of unilateral eye muscle surgery.