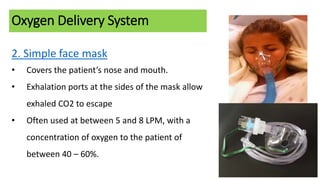
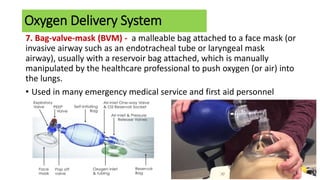
Oxygen therapy involves the administration of oxygen to maintain adequate tissue oxygenation levels and minimize workload on the cardiopulmonary system. Oxygen is indicated when a patient has documented hypoxemia with oxygen saturation below 90% or a partial pressure of oxygen below 60 mmHg. Various oxygen delivery systems can be used including nasal cannulas, face masks, Venturi masks, and non-rebreather masks to provide different concentrations of oxygen from 24-100% at flow rates of 2-10 LPM. Potential complications of oxygen therapy include oxygen toxicity, depression of ventilation, retinopathy of prematurity, absorption atelectasis, and fire hazards.