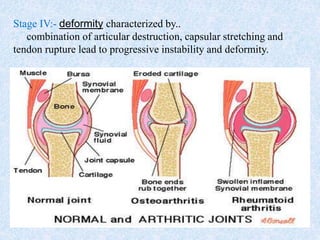
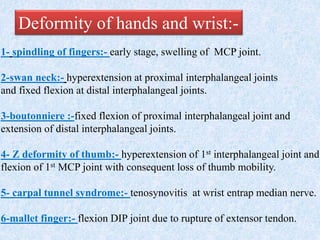
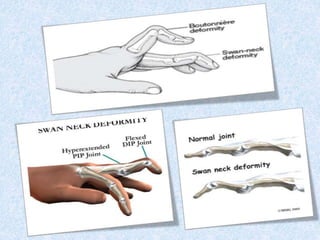
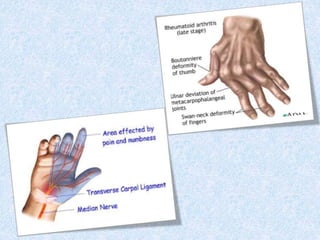
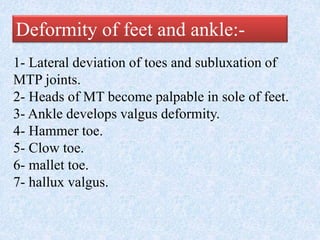
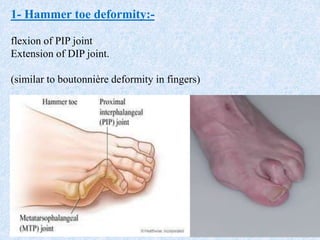
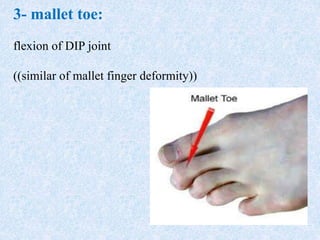
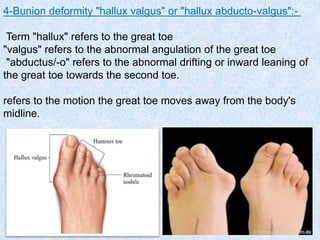
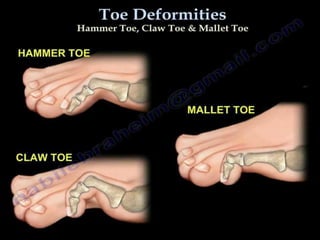
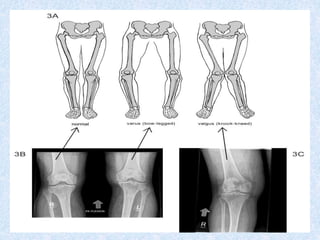
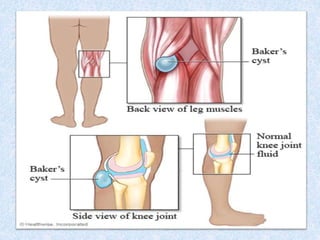
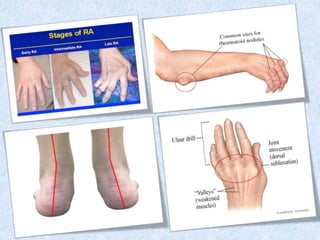
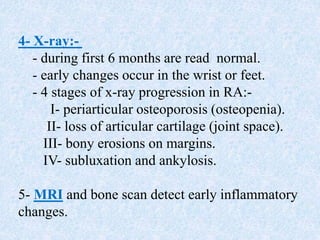
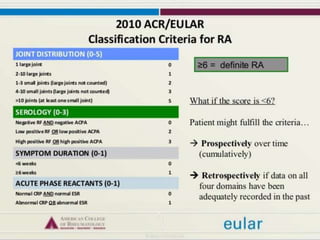
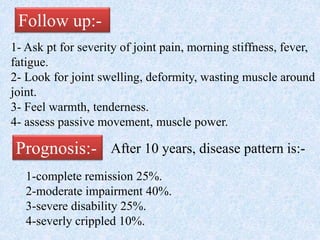
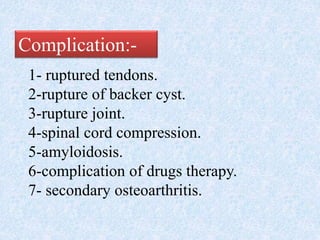
Chronic symmetrical polyarthritis is characterized by chronic joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It is associated with inflammation of the synovium of peripheral joints. The disease course involves exacerbations and remissions. It predominantly affects women between ages 20-40. Causes include genetic factors and autoimmunity. Advanced stages involve destruction of articular cartilage and bone erosion, leading to deformities such as finger spindling and foot deformities. Diagnosis is based on clinical features and meeting criteria for rheumatoid arthritis including joint swelling and morning stiffness. Management involves pharmacological treatments like NSAIDs and DMARDs as well as surgery.