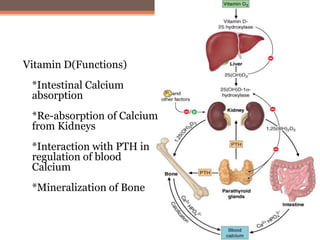
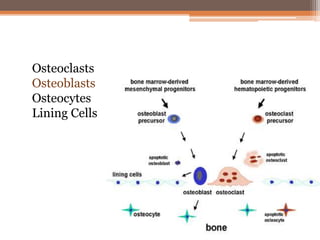
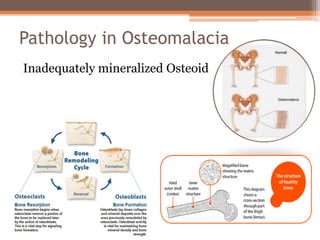
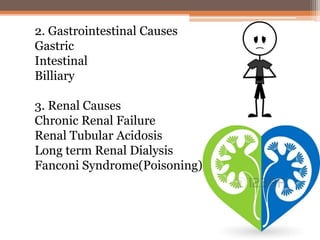
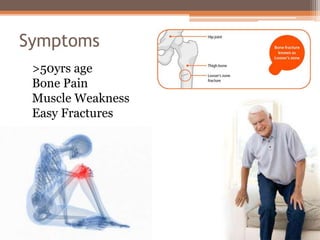
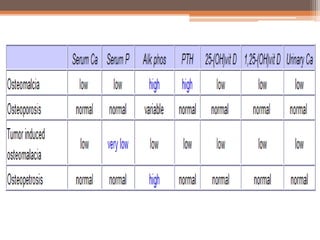
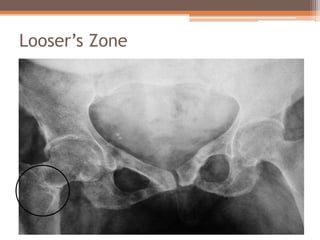
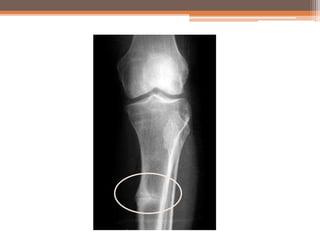
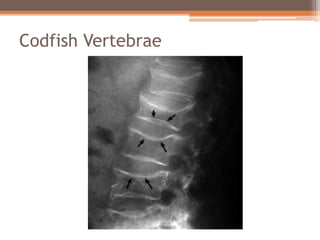
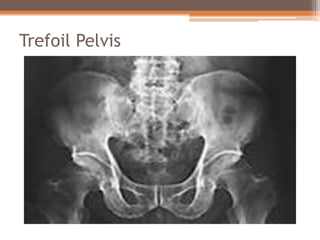
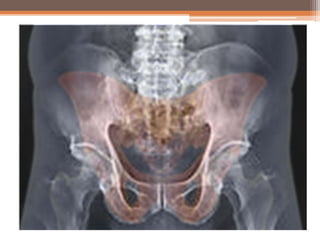
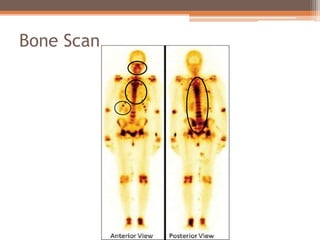
Osteomalacia is a softening of the bones due to vitamin D deficiency which impairs bone mineralization. It commonly affects elderly individuals, those with a family history of rickets, people of black or South Asian descent, and patients with gastrointestinal, renal or tumor conditions that interfere with vitamin D absorption or metabolism. Symptoms include bone pain, muscle weakness, and increased risk of fractures. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure calcium, phosphate, vitamin D, and alkaline phosphatase levels. Treatment focuses on increasing vitamin D through sun exposure, dietary sources, and supplementation.




![Bone Mineralization
Bone Mineral Hydroxyapatite
[Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]
Vitamin D(Metabolism)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osteomalacia-150307044638-conversion-gate01/85/Osteomalacia-5-320.jpg)