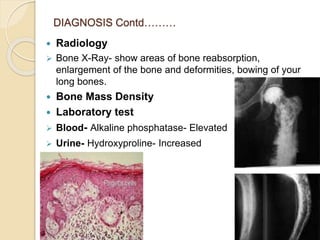
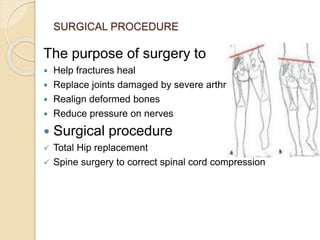
Paget's disease is a chronic bone disorder characterized by abnormal bone metabolism, leading to enlarged and deformed bones that can cause pain, fractures, and joint issues. Its exact cause is unknown, but genetics and possible viral infections are linked to its development. Management includes education, multidisciplinary care, pharmacological treatment, and possibly surgery for severe cases.